[ad_1]
M.T. Aguado
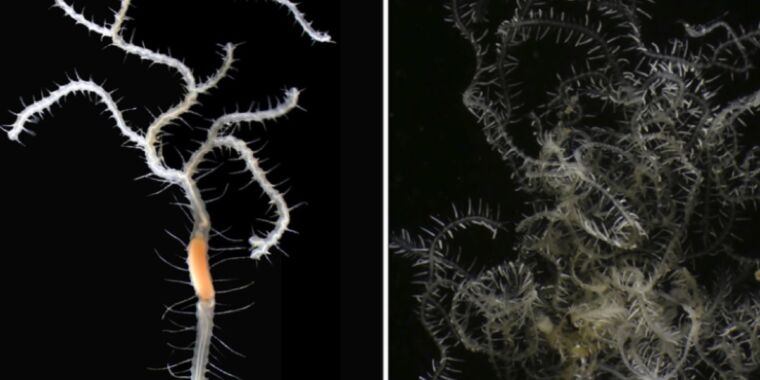
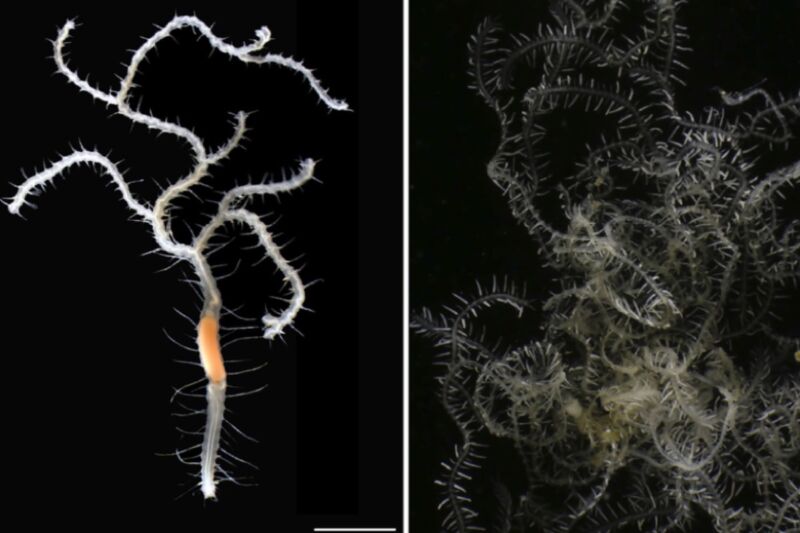
Within the 2019 blockbuster movie, Godzilla: King of the Monsters, everybody’s favourite kaiju, Godzilla, battled one other titan named King Ghidorah, a monster notable for its three heads. Now biologists have found a brand new species of marine worm that has one head however a physique that may department out into a number of posterior ends, in keeping with a current paper revealed within the journal Organisms Variety & Evolution. So naturally the biologists named the brand new species after Godzilla’s legendary adversary: Ramisyllis kingghidorahi.
“King Ghidorah is a branching fictitious animal that may regenerate its misplaced ends, so we thought this was an acceptable title for the brand new species of branching worm,” stated co-author M. Teresa Aguado of the College of Göttingen. The truth is, the director of the primary Ghidorah-centric function movie in 1964, Ishiro Honda, stated his monster was a contemporary tackle a legendary eight-headed and eight-tailed dragon/serpent in Japanese folklore referred to as Yamata no Orochi.
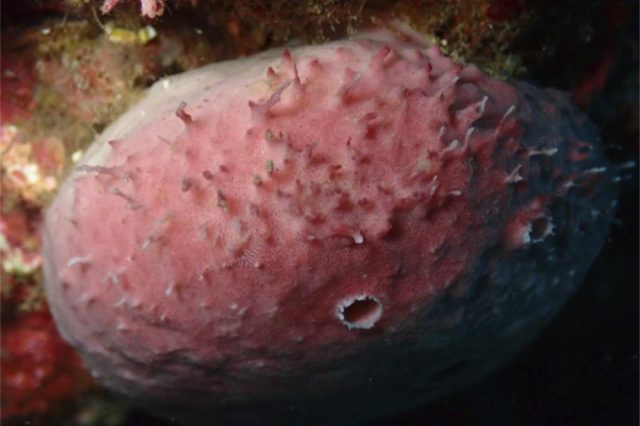
In line with Aguado and her co-authors, solely two different species of those uncommon branching worms have been found. Again in 1879, an beginner naturalist named Charles Macintosh reported the invention of a “remarkably branched Syllid” (dubbed Syllis ramosa). The creature was discovered lurking inside a glass sea sponge within the Philippines through the Challenger pure historical past expedition. Syllis ramosa was the primary recognized occasion of an annelid species with a “randomly branching asymmetrical physique.”
The second species of branching marine worm (Ramisyllis multicaudata) wasn’t discovered till 2012, noticed within the coastal shallows of Darwin, Northern Australia. Like Syllis ramosa, the second species additionally had a randomly branching asymmetrical physique and lived contained in the labyrinthine canals of sea sponges. And each reproduce asexually by a course of referred to as schizogamy. The worms type posterior segments with buds (or gametes) which might develop options like eyes and sensory organs. As soon as shaped, the gametes can detach and swim freely, and the posterior ends can regenerate.

Toru Miura
This new third species was found at Shukunegi Level on Sado Island in Japan, additionally inhabiting sponges. The Japanese group despatched photos of the worms to Aguado, who immediately acknowledged the worms’ novelty and arranged a 2019 expedition to the island to collect samples and examine the creatures in higher element.
“We have been astonished to seek out one other of those weird creatures with just one head and a physique shaped from a number of branching,” stated Aguado. “The primary worm was regarded as distinctive. This discovery reveals the next range of those tree-like animals than anybody anticipated.”
Aguado and her co-authors mixed their interdisciplinary experience to study extra concerning the new species. Their investigation included molecular evaluation that exposed Ramisyllis multicaudata and Ramisyllis kingghidorahi share a standard evolutionary ancestor. However there are nonetheless some genetic divergences, significantly concerning the form of sure physique segments.
The authors counsel that each species could have inherited the distinctive lengthy asymmetrical physique from their final frequent ancestor. which had tailored to outlive contained in the branching canals of a sponge. “The ramified our bodies of the branching syllids would possibly mirror the intricate labyrinth of the sponge canal system, with the power to supply new totally developed segments permitting the worm to discover the canals,” the authors wrote.
Loads of mysteries stay about these uncommon species of branching worms, which would be the focus of future analysis. “Scientists do not but perceive the character of the connection between the branching worm and its host sponge: is it a symbiotic relationship the place each creatures one way or the other profit?” stated Aguado. “And the way do the worms handle to feed to take care of their big our bodies having only one tiny mouth of their single head?”
DOI: Organisms Variety & Evolution, 2022. 10.1007/s13127-021-00538-4 (About DOIs).
[ad_2]