[ad_1]
Scientific traits of the topics
A complete of 150 plasma samples have been used to establish metabolic variations between SAP (50 samples), MAP (50 samples), and wholesome controls (50 samples). The scientific traits have been proven in Further file 1: Desk S1. There was no important distinction within the period of stomach ache when put next between teams (p > 0.05).
Isolation and characterization of EVs
For every pattern, EVs have been remoted from 20 µL of plasma by utilizing EXODUS. Every plasma pattern was diluted 250-fold to remove the adversarial results of clogging and aggregation close to isolation time and purity. As proven in Further file 1: Fig. S1, the remoted EVs have been characterised by TEM and NTA. TEM confirmed that the EVs had a typical cup-shaped construction. The dimensions distribution of the remoted EVs introduced a clean unimodal curve in keeping with NTA, with peaks starting from 80 to 100 nm. There have been no important variations between the EVs from SAP, MAP, and wholesome controls, close to imply diameter and measurement distribution.
Differential metabolic profiles of EVs remoted from SAP, MAP, and wholesome management teams
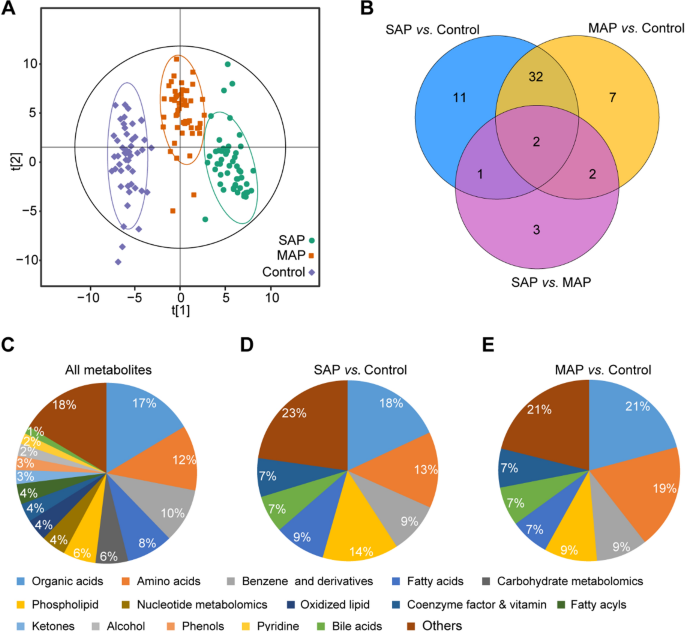
A complete of 313 metabolites have been efficiently detected by broadly focused metabolomics primarily based on ultra-performance LC-MS/MS. The OPLS-DA mannequin, which is delicate to much less correlated variables, was used to indicate the differential abundance of metabolites throughout all three teams. Among the many 313 detected metabolites, differential metabolites have been screened out in keeping with the FC worth (≥ 1.5). There was a big number of metabolites within the EVs remoted from SAP, MAP, and wholesome management teams (Fig. 2 A). Correspondingly, the expression of metabolites in EVs remoted from the SAP and MAP teams have been each considerably completely different from these within the wholesome management group (Fig. 2B). There have been apparent variations between exosomal metabolites from sufferers and wholesome samples, whereas the metabolite profiles of SAP and MAP teams confirmed each overlaps and variations; this requires additional evaluation. The metabolites detected have been largely natural acids and their derivatives, amino acid metabolomics, benzene and substituted derivatives, carbohydrate metabolomics, and lipid species from fatty acids, phospholipids, and oxidized lipids (Fig. 2C), thus indicating that these metabolites have been frequent parts of EVs. Among the many differential metabolites, probably the most considerable metabolite courses have been natural acids, amino acids, benzene and its derivatives, phospholipids, fatty acids, bile acids, and coenzyme elements and nutritional vitamins; these accounted for many of the detected differential metabolites (Fig. 2D and E). The proportions of fatty acids among the many differential metabolites in SAP samples have been greater than these in MAP, whereas extra natural acids, amino acids, and phospholipids differed in MAP. Variations in EV metabolites between the SAP and MAP teams have been smaller than these between illness samples and wholesome management samples.
Characterization of metabolic profiles from samples of SAP, MAP, and wholesome controls. A The OPLS-DA evaluation and B the Venn diagram of the differential metabolites between the SAP, MAP, and wholesome management teams. Composition of (C) the general detected metabolites, and the differential metabolites discovered within the comparisons of (D) SAP vs. wholesome management and (E) MAP vs. wholesome management, respectively
It’s properly established that pancreatic illness can affect the metabolism of amino acids (Fig. 3B and Further file 1: Fig. S2C). For instance, we discovered that valine was considerably down-regulated in each the SAP and MAP teams. Pancreatic illness is carefully related to the down-regulation of valine. Moreover, the pathway underlying the biosynthesis of valine is concerned within the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis [24]. As well as, valine is a part of pancreatic juice [30]; pancreatic insufficiency may be answerable for valine reductions. One other instance is the up-regulation of glutamic acid’s derivatives, which can also be a symptom of pancreatic illness [28]. Bile acids and choline have been additionally discovered to markedly alter in diseased samples. Glycoursodeoxycholic acid was down-regulated, which could intrude with lipid digestion. The poisonous impact of bile acids on acinar cells additionally induces the formation of pro-inflammatory mediators, though the scientific significance of this course of has but to be decided [7]. We detected an general discount within the ranges of phosphatidylcholines in pancreatitis samples. Choline metabolism performs a major function in inflammatory responses and may change varied pancreatic ailments [28].
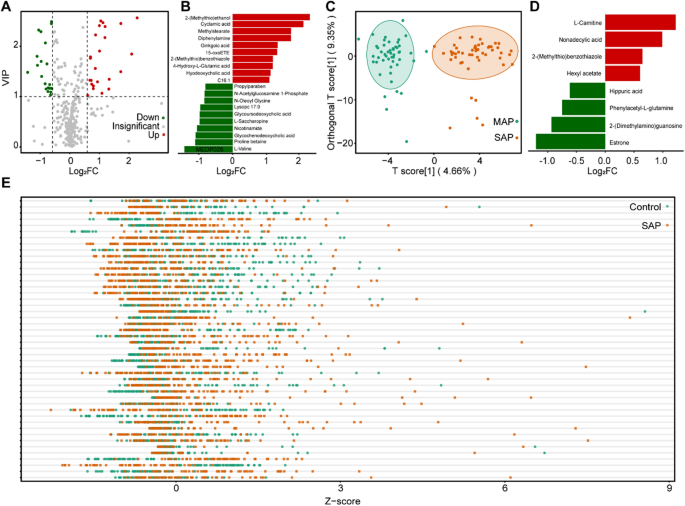
Evaluation of the differential metabolites compared to SAP, MAP, and wholesome controls. A The volcano plot displaying the differential metabolites in SAP EVs in comparison with wholesome management; B The highest 20 differential metabolites of the SAP and wholesome management teams primarily based on the FC values; C The OPLS-DA rating plot for distinguishing SAP and MAP teams; D The highest 8 differential metabolites of the SAP and MAP teams. E The z-score plot of differential metabolites within the SAP and MAP teams
Earlier research have additionally demonstrated that modifications in bile acids, phosphatidylcholine, and amino acids happen in acute pancreatitis [27, 31, 32], thus confirming our current findings. Nevertheless, few researchers have investigated variations in metabolites between extreme and delicate instances.
Differential EV metabolites between SAP and MAP
In comparison with EVs from wholesome controls, a complete variety of 46 and 43 differential metabolites have been detected in SAP-EVs and MAP-EVs, respectively. Of those, 34 metabolites have been shared by the SAP and MAP teams (Figs. 2B and 3A, and Further file 1: Fig. S2A). The metabolites displaying the best modifications in samples of illness sufferers included natural acids, bile acids, amino acids, benzene, substituted derivatives, and others (Fig. 3B and Further file 1: Fig. S2B). It was clear that there have been important modifications in metabolites related to irritation, the pancreas, and digestion.
We additional evaluated the metabolic traits of EVs between SAP and MAP teams and investigated the metabolic traits of SAP- and MAP-EVs. OPLS-DA rating plots revealed general variations in metabolites between the SAP and MAP teams (Fig. 3C). The metabolic profiles of EVs have been in contrast between the SAP and MAP teams, and we discovered that these teams shared many differential metabolites when in comparison with wholesome management samples. Additionally, some metabolites confirmed distinctive modifications solely within the SAP or MAP teams (Fig. 2B). A complete of eight differential metabolites have been detected and confirmed important variations (Fig. 3D), together with estrone, non-adecylic acid, phenylacetyl-L-glutamine, L-carnitine, hippuric acid, 2-(dimethylamino)-guanosine, hexyl acetate, and 2-(methylthio)benzothiazole. We additionally created a Z-score plot to current the general variations between the 2 teams (Fig. 3E).
Based mostly on these outcomes, it was clear that the metabolomic traits of EVs can mirror the metabolic traits of sufferers with SAP and MAP. Moreover, the distinctive differential metabolites present in sufferers with SAP indicated the distinct roles of those metabolites within the genesis and growth of SAP. Consequently, there’s a sturdy risk that EV-carried metabolites could also be used to establish new biomarkers for the prognosis of SAP.
Choosing potential biomarkers for distinguishing SAP and MAP
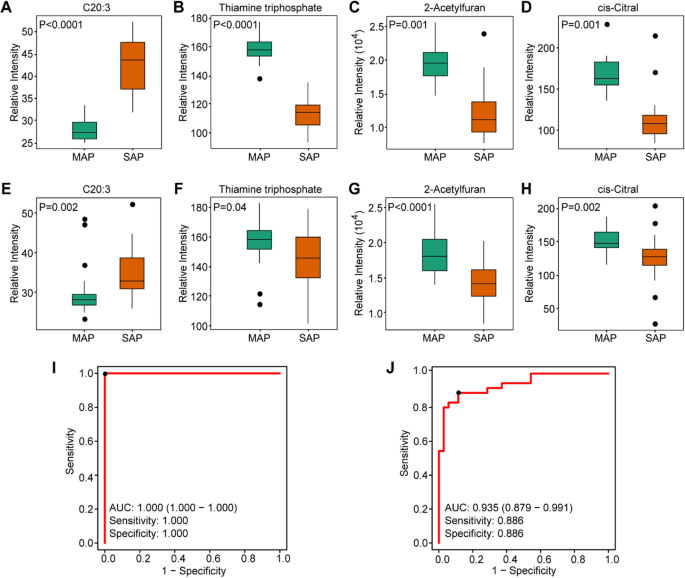
Plasma EVs have been additional chosen as potential metabolic biomarker cargo to tell apart between samples with SAP and MAP. In response to OPLS-DA evaluation, samples from the SAP and MAP teams separated properly (Further file 1: Fig. S2C). We carried out random forest evaluation, by which 30 instances (15 SAP and 15 MAP samples) have been used as a discovery set to establish metabolic biomarker candidates for the prognosis of SAP, and 70 instances (35 SAP and 35 MAP samples) have been assigned as a validation set. Within the discovery set, the VIP worth was the primary parameter used to evaluate the contribution of various variables to the classification of information, together with the FDR worth. We recognized 9 metabolites that happy the screening circumstances with VIP worth> 1.0 and FDR < 0.05 (Further file 1: Desk S2).Then the 9 differential metabolites have been ranked so as of VIP worth from highest to lowest, and the primary 4 metabolites have been recognized as potential biomarkers between the SAP and MAP teams: cis-11,14,17-eicosatrienoic acid (C20:3), thiamine triphosphate, 2-acetyl furan, and cis-citral (Fig. 4A–D).These candidates additionally confirmed exceptional variations when put next between SAP and MAP samples within the validation set (Fig. 4E–H). Receiver-operating attribute curve (ROC) evaluation was then used to additional assess the efficiency of the candidates. The realm below the curve (AUC) values for every candidate was> 0.90 within the discovery set and > 0.68 within the validation set (Further file 1: Fig. S3). Extra important variations have been obtained by combining the candidates moderately than utilizing the metabolites individually (Fig. 4I, J). When metabolites have been mixed, the AUC values elevated to 1.00 and 0.935 for the invention and validation units, respectively. Moreover, the sensitivity and specificity have been each 1.00 within the discovery set and 0.886 within the validation set. Therefore, the modifications in expression ranges of the 4 candidates confirmed considerably distinction between SAP and MAP samples.
Identification of metabolite biomarkers for distinguishing SAP and MAP. Relative intensities of the outlined biomarker candidates within the discovery set (A–D) and the validation set (E–H). (I–J) ROC efficiency primarily based on the chosen metabolic markers (C20:3, thiamine triphosphate, 2-acetyl furan, and cis-citral) within the discovery and validation units, respectively
[ad_2]