[ad_1]
Organizations communicate of operational reporting and analytics as the subsequent technical problem in bettering enterprise processes and effectivity. In a world the place everyone seems to be turning into an analyst, stay dashboards floor up-to-date insights and operationalize real-time information to supply in-time decision-making assist throughout a number of areas of a company. We’ll take a look at what it takes to construct operational dashboards and reporting utilizing normal information visualization instruments, like Tableau, Grafana, Redash, and Apache Superset. Particularly, we’ll be specializing in utilizing these BI instruments on information saved in DynamoDB, as now we have discovered the trail from DynamoDB to information visualization software to be a typical sample amongst customers of operational dashboards.
Creating information visualizations with present BI instruments, like Tableau, might be a superb match for organizations with fewer assets, much less strict UI necessities, or a want to shortly get a dashboard up and working. It has the additional benefit that many analysts on the firm are already acquainted with find out how to use the software. In case you are serious about crafting your personal customized dashboard, examine Customized Dwell Dashboards on DynamoDB as a substitute.
We think about a number of approaches, all of which use DynamoDB Streams however differ in how the dashboards are served:
1. DynamoDB Streams + Lambda + Kinesis Firehose + Redshift
2. DynamoDB Streams + Lambda + Kinesis Firehose + S3 + Athena
3. DynamoDB Streams + Rockset
We’ll consider every strategy on its ease of setup/upkeep, information latency, question latency/concurrency, and system scalability so you’ll be able to choose which strategy is greatest for you based mostly on which of those standards are most necessary on your use case.
Concerns for Constructing Operational Dashboards Utilizing Customary BI Instruments
Constructing stay dashboards is non-trivial as any answer must assist extremely concurrent, low latency queries for quick load occasions (or else drive down utilization/effectivity) and stay sync from the information sources for low information latency (or else drive up incorrect actions/missed alternatives). Low latency necessities rule out instantly working on information in OLTP databases, that are optimized for transactional, not analytical, queries. Low information latency necessities rule out ETL-based options which improve your information latency above the real-time threshold and inevitably result in “ETL hell”.
DynamoDB is a completely managed NoSQL database supplied by AWS that’s optimized for level lookups and small vary scans utilizing a partition key. Although it’s extremely performant for these use circumstances, DynamoDB just isn’t a sensible choice for analytical queries which usually contain massive vary scans and complicated operations resembling grouping and aggregation. AWS is aware of this and has answered clients requests by creating DynamoDB Streams, a change-data-capture system which can be utilized to inform different providers of recent/modified information in DynamoDB. In our case, we’ll make use of DynamoDB Streams to synchronize our DynamoDB desk with different storage techniques which can be higher suited to serving analytical queries.
To construct your stay dashboard on prime of an present BI software basically means you must present a SQL API over a real-time information supply, after which you should use your BI software of selection–Tableau, Superset, Redash, Grafana, and many others.–to plug into it and create your entire information visualizations on DynamoDB information. Subsequently, right here we’ll give attention to making a real-time information supply with SQL assist and go away the specifics of every of these instruments for one more publish.
Kinesis Firehose + Redshift
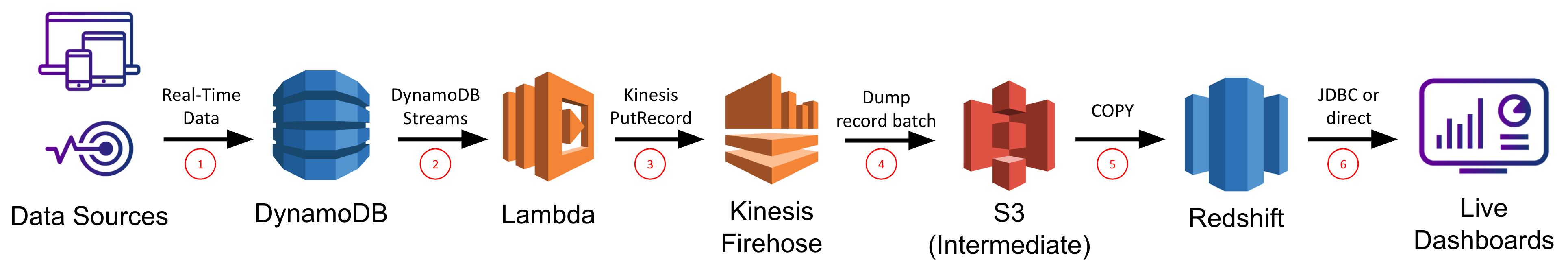
We’ll begin off this finish of the spectrum by contemplating utilizing Kinesis Firehose to synchronize your DynamoDB desk with a Redshift desk, on prime of which you’ll run your BI software of selection. Redshift is AWS’s information warehouse providing that’s particularly tailor-made for OLAP workloads over very massive datasets. Most BI instruments have express Redshift integrations obtainable, and there’s a typical JDBC connection to can be utilized as properly.
The very first thing to do is create a brand new Redshift cluster, and inside it create a brand new database and desk that shall be used to carry the information to be ingested from DynamoDB. You may connect with your Redshift database by means of a typical SQL consumer that helps a JDBC connection and the PostgreSQL dialect. You’ll have to explicitly outline your desk with all area names, information varieties, and column compression varieties at this level earlier than you’ll be able to proceed.
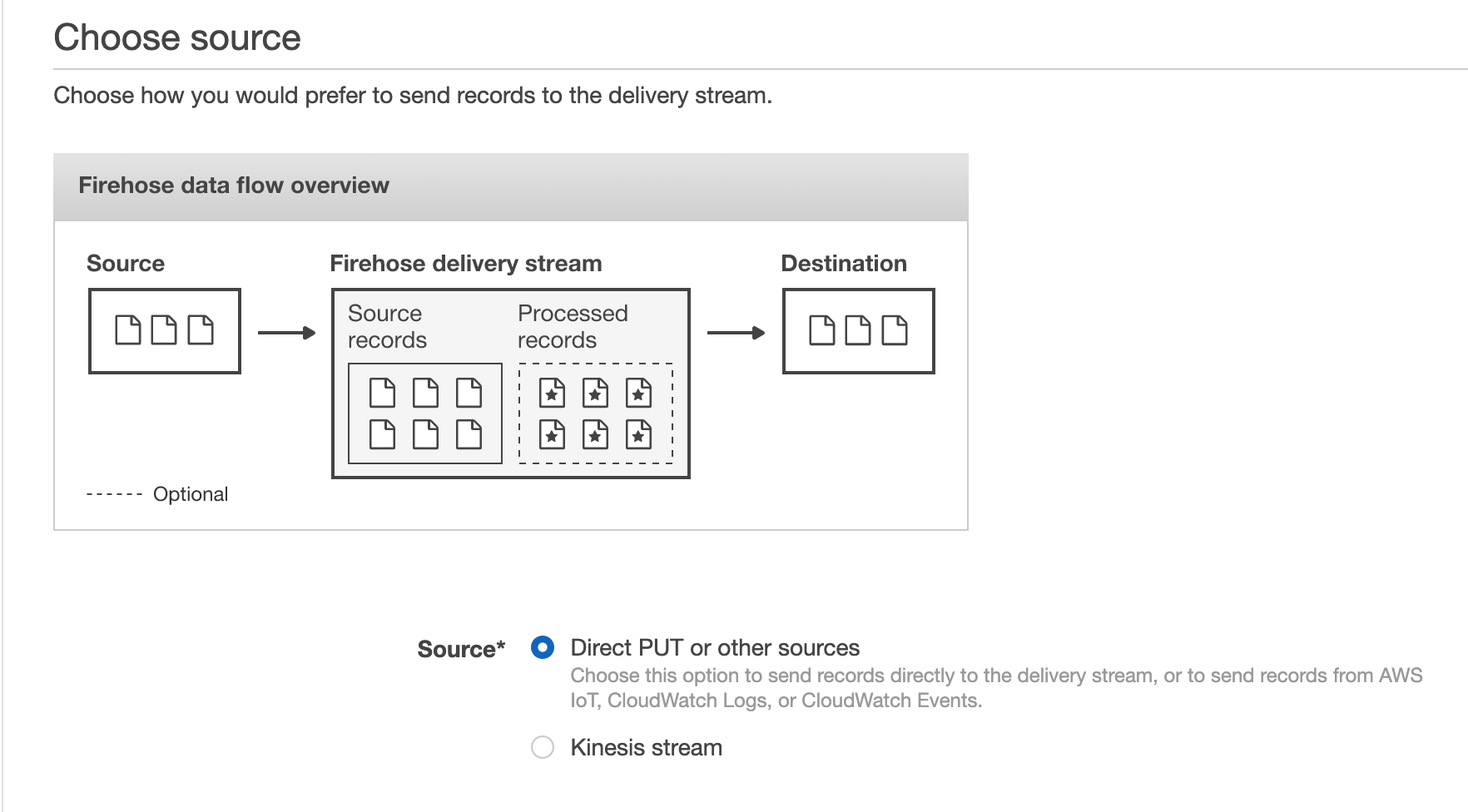
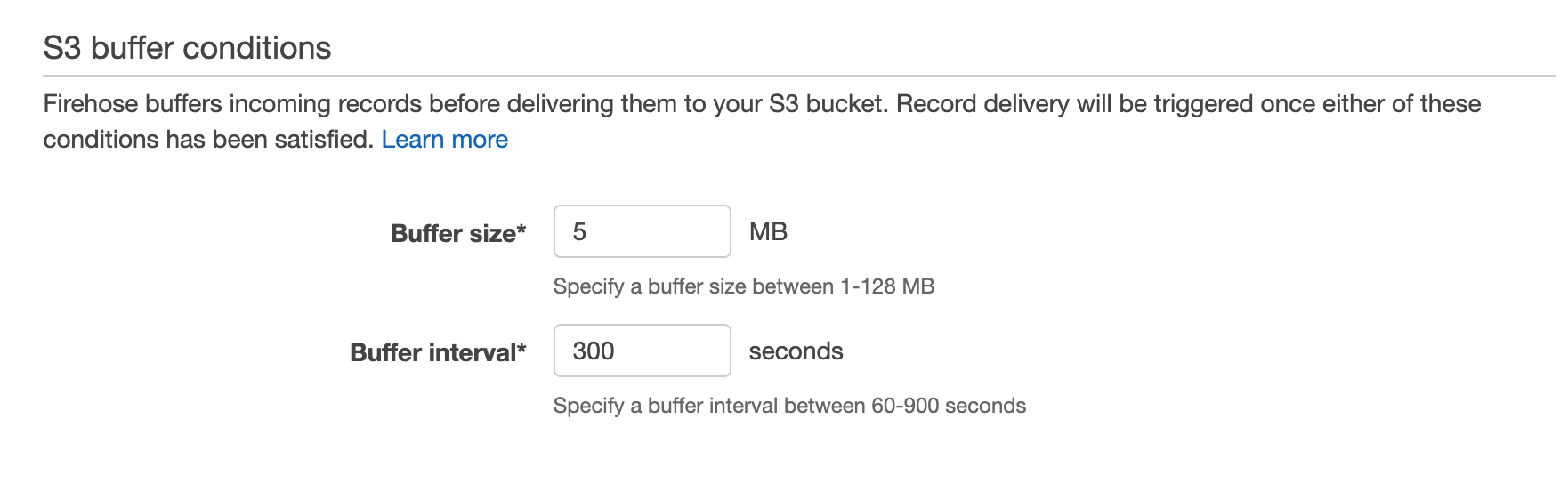
Subsequent, you’ll must go to the Kinesis dashboard and create a brand new Kinesis Firehose, which is the variant AWS offers to stream occasions to a vacation spot bucket in S3 or a vacation spot desk in Redshift. We’ll select the supply choice Direct PUT or different sources, and we’ll choose our Redshift desk because the vacation spot. Right here it provides you some useful optimizations you’ll be able to allow like staging the information in S3 earlier than performing a COPY command into Redshift (which ends up in fewer, bigger writes to Redshift, thereby preserving valuable compute assets in your Redshift cluster and supplying you with a backup in S3 in case there are any points throughout the COPY). We are able to configure the buffer measurement and buffer interval to regulate how a lot/typically Kinesis writes in a single chunk. For instance, a 100MB buffer measurement and 60s buffer interval would inform Kinesis Firehose to write down as soon as it has obtained 100MB of knowledge, or 60s has handed, whichever comes first.
Lastly, you’ll be able to arrange a Lambda perform that makes use of the DynamoDB Streams API to retrieve current adjustments to the DynamoDB desk. This perform will buffer these adjustments and ship a batch of them to Kinesis Firehose utilizing its PutRecord or PutRecordBatch API. The perform would look one thing like
exports.handler = async (occasion, context) => {
for (const file of occasion.Data) {
let platform = file.dynamodb['NewImage']['platform']['S'];
let quantity = file.dynamodb['NewImage']['amount']['N'];
let information = ... // format in keeping with your Redshift schema
var params = {
Information: information
StreamName: 'check'
PartitionKey: '1234'
};
kinesis.putRecord(params, perform(err, information) {
if (err) console.log(err, err.stack); // an error occurred
else console.log(information); // profitable response
});
}
return `Efficiently processed ${occasion.Data.size} information.`;
};
Placing this all collectively we get the next chain response every time new information is put into the DynamoDB desk:
- The Lambda perform is triggered, and makes use of the DynamoDB Streams API to get the updates and writes them to Kinesis Firehose
- Kinesis Firehose buffers the updates it will get and periodically (based mostly on buffer measurement/interval) flushes them to an intermediate file in S3
- The file in S3 is loaded into the Redshift desk utilizing the Redshift COPY command
- Any queries towards the Redshift desk (e.g. from a BI software) mirror this new information as quickly because the COPY completes
On this manner, any dashboard constructed by means of a BI software that’s built-in with Redshift will replace in response to adjustments in your DynamoDB desk.
Professionals:
- Redshift can scale to petabytes
- Many BI instruments (e.g. Tableau, Redash) have devoted Redshift integrations
- Good for complicated, compute-heavy queries
- Primarily based on acquainted PostgreSQL; helps full-featured SQL, together with aggregations, sorting, and joins
Cons:
- Must provision/keep/tune Redshift cluster which is pricey, time consuming, and fairly difficult
- Information latency on the order of a number of minutes (or extra relying on configurations)
- Because the DynamoDB schema evolves, tweaks shall be required to the Redshift desk schema / the Lambda ETL
- Redshift pricing is by the hour for every node within the cluster, even in case you’re not utilizing them or there’s little information on them
- Redshift struggles with extremely concurrent queries
TLDR:
- Think about this feature in case you don’t have many lively customers in your dashboard, don’t have strict real-time necessities, and/or have already got a heavy funding in Redshift
- This strategy makes use of Lambdas and Kinesis Firehose to ETL your information and retailer it in Redshift
- You’ll get good question efficiency, particularly for complicated queries over very massive information
- Information latency received’t be nice although and Redshift struggles with excessive concurrency
- The ETL logic will most likely break down as your information adjustments and want fixing
- Administering a manufacturing Redshift cluster is a big enterprise
For extra info on this strategy, try the AWS documentation for loading information from DynamoDB into Redshift.
S3 + Athena
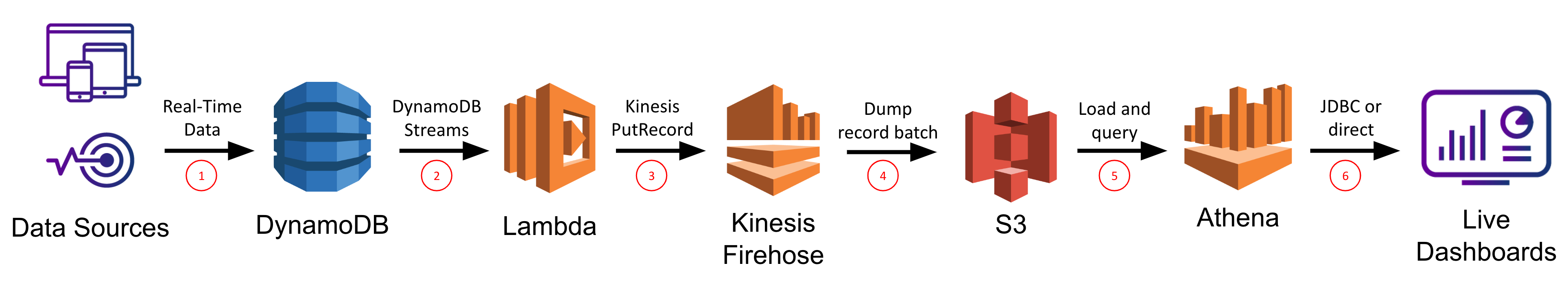
Subsequent we’ll think about Athena, Amazon’s service for working SQL on information instantly in S3. That is primarily focused for rare or exploratory queries that may tolerate longer runtimes and save on price by not having the information copied right into a full-fledged database or cache like Redshift, Redis, and many others.
Very similar to the earlier part, we are going to use Kinesis Firehose right here, however this time it is going to be used to shuttle DynamoDB desk information into S3. The setup is identical as above with choices for buffer interval and buffer measurement. Right here this can be very necessary to allow compression on the S3 recordsdata since that can result in each sooner and cheaper queries since Athena fees you based mostly on the information scanned. Then, just like the earlier part, you’ll be able to register a Lambda perform and use the DynamoDB streams API to make calls to the Kinesis Firehose API as adjustments are made to our DynamoDB desk. On this manner you should have a bucket in S3 storing a duplicate of your DynamoDB information over a number of compressed recordsdata.
Word: You may moreover save on price and enhance efficiency by utilizing a extra optimized storage format and partitioning your information.
Subsequent within the Athena dashboard you’ll be able to create a brand new desk and outline the columns there both by means of the UI or utilizing Hive DDL statements. Like Hive, Athena has a schema on learn system, which means as every new file is learn in, the schema is utilized to it (vs. being utilized when the file is written).
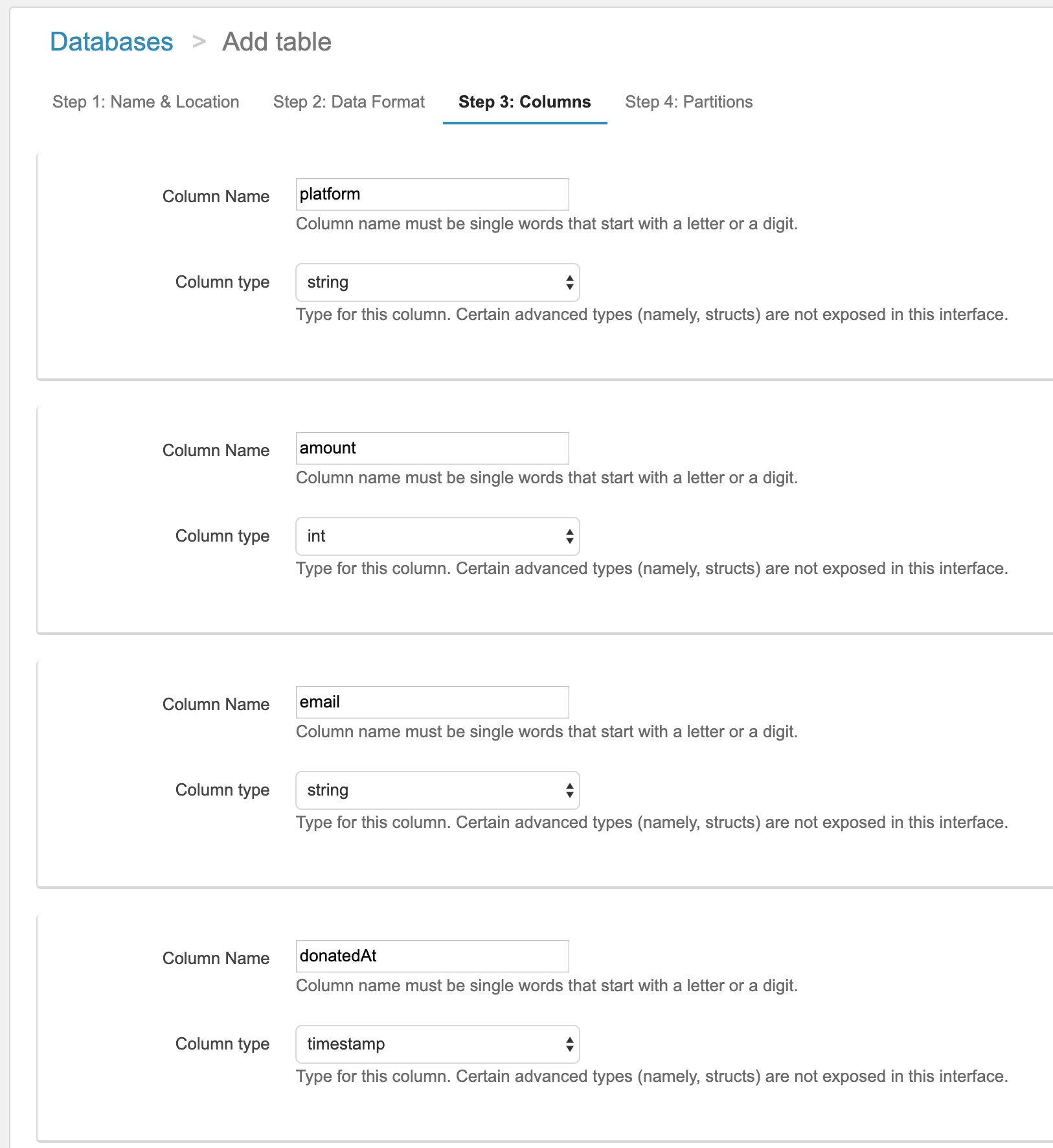
As soon as your schema is outlined, you’ll be able to submit queries by means of the console, by means of their JDBC driver, or by means of BI software integrations like Tableau and Amazon Quicksight. Every of those queries will result in your recordsdata in S3 being learn, the schema being utilized to all of information, and the question end result being computed throughout the information. Because the information just isn’t optimized in a database, there are not any indexes and studying every file is dearer for the reason that bodily format just isn’t optimized. Because of this your question will run, however it would tackle the order of minutes to probably hours.
Professionals:
- Works at massive scales
- Low information storage prices since the whole lot is in S3
- No always-on compute engine; pay per question
Cons:
- Very excessive question latency– on the order of minutes to hours; can’t use with interactive dashboards
- Must explicitly outline your information format and format earlier than you’ll be able to start
- Blended varieties within the S3 recordsdata attributable to DynamoDB schema adjustments will result in Athena ignoring information that don’t match the schema you specified
- Until you place within the time/effort to compress your information, ETL your information into Parquet/ORC format, and partition your information recordsdata in S3, queries will successfully at all times scan your entire dataset, which shall be very gradual and really costly
TLDR:
- Think about this strategy if price and information measurement are the driving components in your design and provided that you’ll be able to tolerate very lengthy and unpredictable run occasions (minutes to hours)
- This strategy makes use of Lambda + Kinesis Firehose to ETL your information and retailer it in S3
- Greatest for rare queries on tons of knowledge and DynamoDB reporting / dashboards that do not should be interactive
Check out this AWS weblog for extra particulars on find out how to analyze information in S3 utilizing Athena.
Rockset

The final choice we’ll think about on this publish is Rockset, a serverless search and analytics service. Rockset’s information engine has sturdy dynamic typing and sensible schemas which infer area varieties in addition to how they modify over time. These properties make working with NoSQL information, like that from DynamoDB, straight ahead. Rockset additionally integrates with each customized dashboards and BI instruments.
After creating an account at www.rockset.com, we’ll use the console to arrange our first integration– a set of credentials used to entry our information. Since we’re utilizing DynamoDB as our information supply, we’ll present Rockset with an AWS entry key and secret key pair that has correctly scoped permissions to learn from the DynamoDB desk we wish. Subsequent we’ll create a group– the equal of a DynamoDB/SQL desk– and specify that it ought to pull information from our DynamoDB desk and authenticate utilizing the mixing we simply created. The preview window within the console will pull a couple of information from the DynamoDB desk and show them to verify the whole lot labored accurately, after which we’re good to press “Create”.
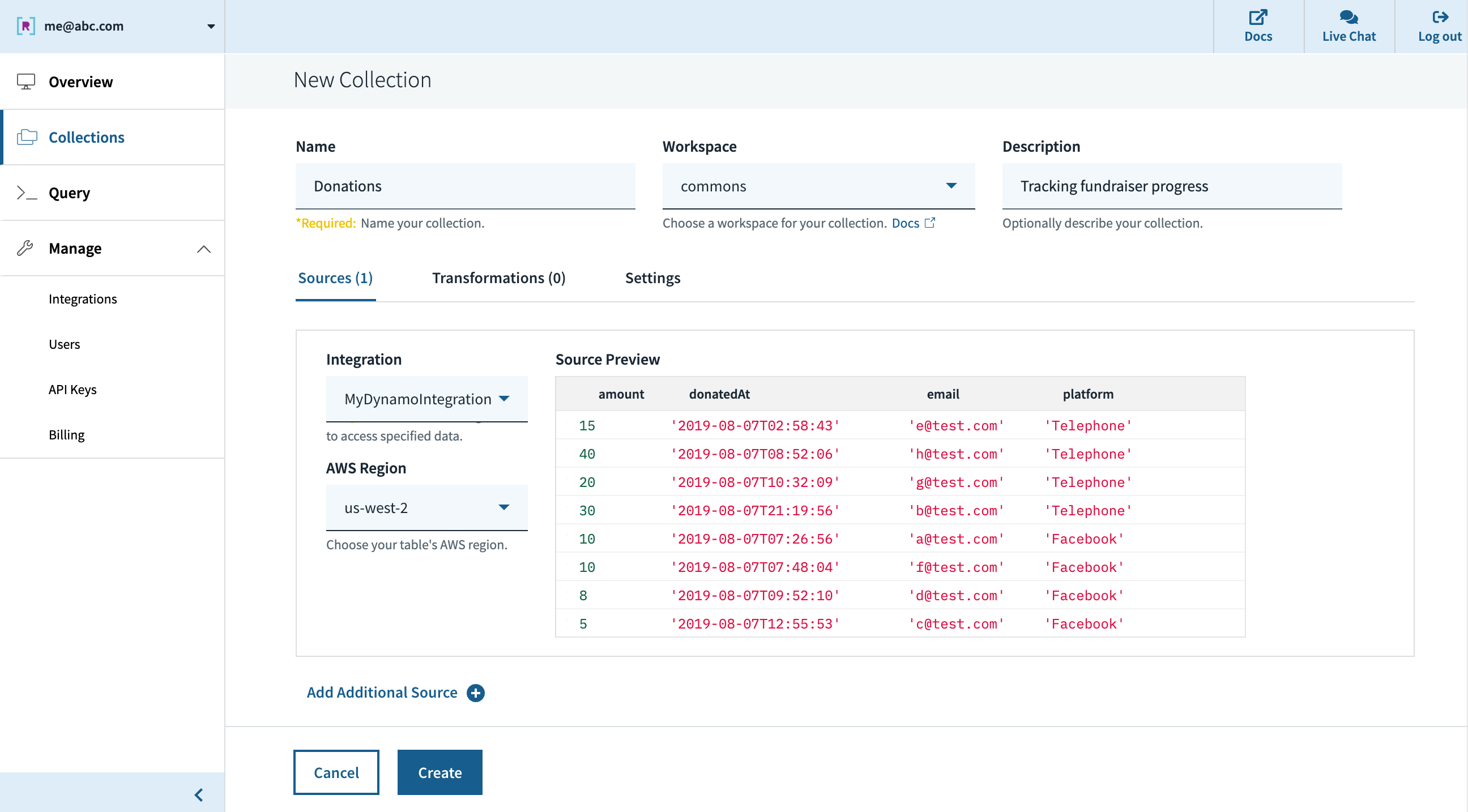
Quickly after, we are able to see within the console that the gathering is created and information is streaming in from DynamoDB. We are able to use the console’s question editor to experiment/tune the SQL queries that shall be utilized in our stay dashboard. Since Rockset has its personal question compiler/execution engine, there may be first-class assist for arrays, objects, and nested information buildings.
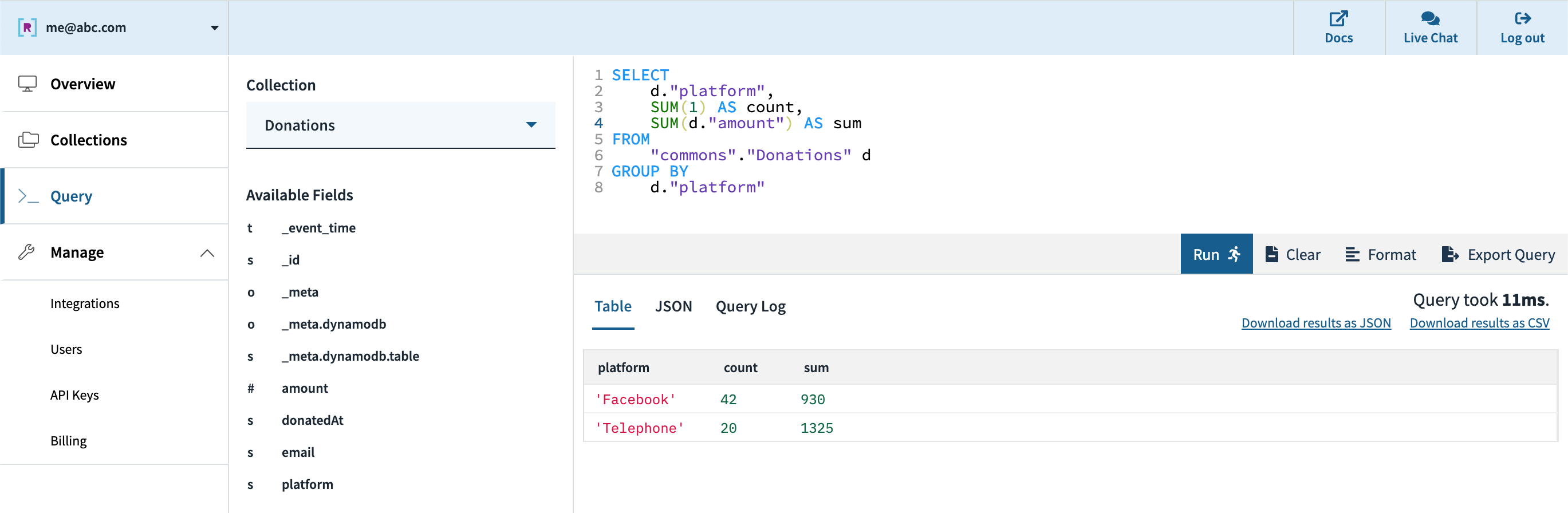
Subsequent, we are able to create an API key within the console which shall be utilized by the dashboard for authentication to Rockset’s servers. Our choices for connecting to a BI software like Tableau, Redash, and many others. are the JDBC driver that Rockset offers or the native Rockset integration for those who have one.
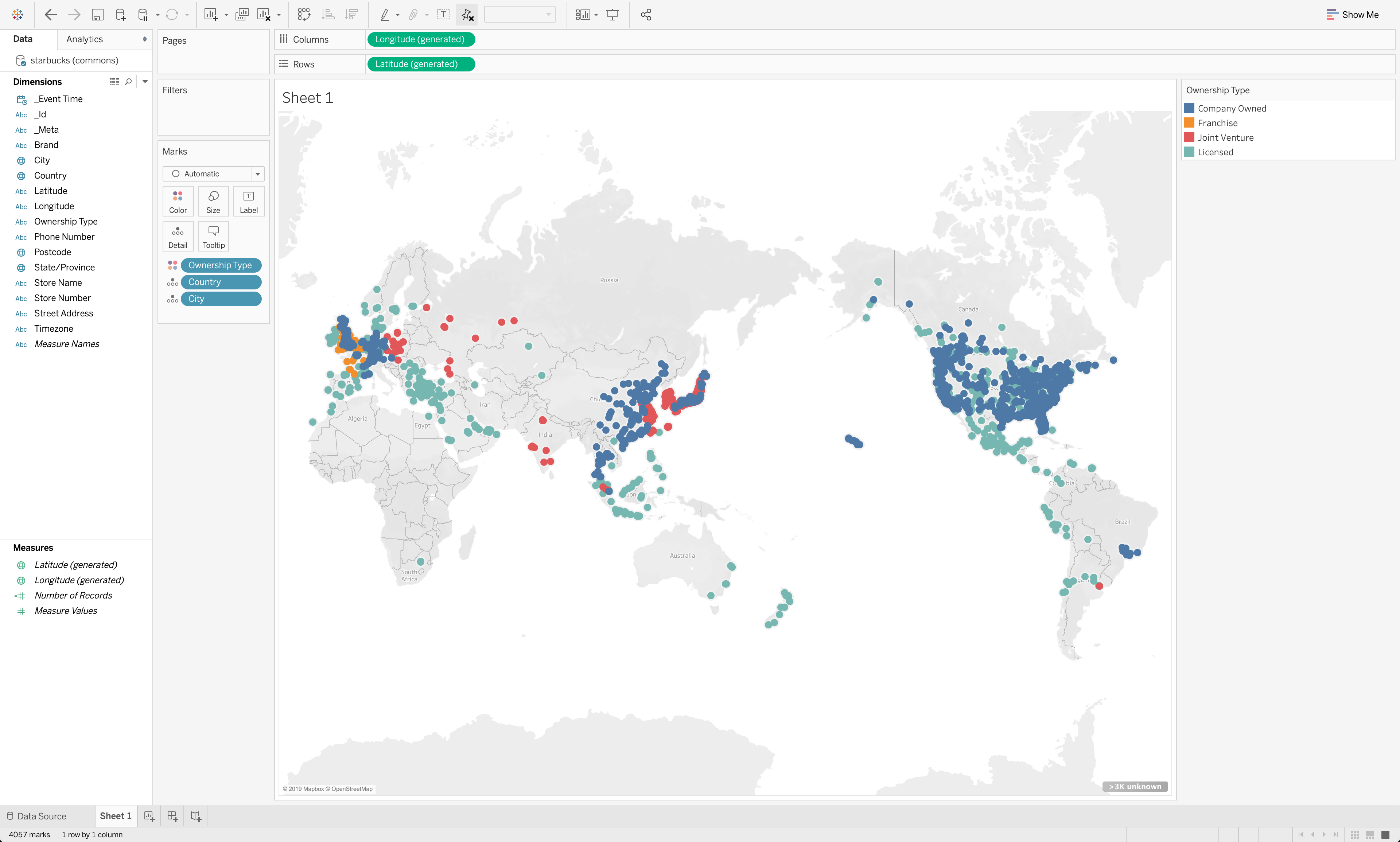
We have now efficiently gone from DynamoDB information to a quick, interactive dashboard on Tableau, or different BI software of selection. Rockset’s cloud-native structure permits it to scale question efficiency and concurrency dynamically as wanted, enabling quick queries even on massive datasets with complicated, nested information with inconsistent varieties.
Professionals:
- Serverless– quick setup, no-code DynamoDB integration, and 0 configuration/administration required
- Designed for low question latency and excessive concurrency out of the field
- Integrates with DynamoDB (and different sources) in real-time for low information latency with no pipeline to keep up
- Sturdy dynamic typing and sensible schemas deal with blended varieties and works properly with NoSQL techniques like DynamoDB
- Integrates with a wide range of BI instruments (Tableau, Redash, Grafana, Superset, and many others.) and customized dashboards (by means of consumer SDKs, if wanted)
Cons:
- Optimized for lively dataset, not archival information, with candy spot as much as 10s of TBs
- Not a transactional database
- It’s an exterior service
TLDR:
- Think about this strategy when you’ve got strict necessities on having the most recent information in your real-time dashboards, must assist massive numbers of customers, or wish to keep away from managing complicated information pipelines
- Constructed-in integrations to shortly go from DynamoDB (and lots of different sources) to stay dashboards
- Can deal with blended varieties, syncing an present desk, and tons of quick queries
- Greatest for information units from a couple of GBs to 10s of TBs
For extra assets on find out how to combine Rockset with DynamoDB, try this weblog publish that walks by means of a extra complicated instance.
Conclusion
On this publish, we thought of a couple of approaches to enabling normal BI instruments, like Tableau, Redash, Grafana, and Superset, for real-time dashboards on DynamoDB, highlighting the professionals and cons of every. With this background, it’s best to be capable to consider which choice is correct on your use case, relying in your particular necessities for question and information latency, concurrency, and ease of use, as you implement operational reporting and analytics in your group.
Different DynamoDB assets:
[ad_2]