[ad_1]
For website positioning specialists, Google’s core updates are a lifestyle. They may occur at the very least as soon as – if not a number of instances – a yr.
Naturally, there will likely be winners and losers.
So whereas Google doesn’t disclose many of the rating components behind the algorithm updates, there are issues we will do to get a better understanding of what’s happening, when it comes to:
- Which web site content material is affected.
- Websites working in your search area.
- End result varieties.
The restrict is your creativeness, your questions (based mostly in your website positioning information), and naturally, your knowledge.
This code will cowl aggregations on the search engine outcomes web page (SERP) degree (inter-site class comparability), and the identical ideas may be utilized to different views of the core replace corresponding to consequence varieties (suppose snippets and different views talked about above).
Utilizing Python To Examine SERPs
The general precept is to match the SERPs earlier than and after the core replace, which can give us some clues as to what’s happening.
We’ll begin by importing our Python libraries:
import re
import time
import random
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import datetime
from datetime import timedelta
from plotnine import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pandas.api.varieties import is_string_dtype
from pandas.api.varieties import is_numeric_dtype
import uritools
pd.set_option('show.max_colwidth', None)
%matplotlib inline
Defining some variables, we’re going to be specializing in ON24.com as they misplaced out to the core replace.
root_domain = 'on24.com' hostdomain = 'www.on24.com' hostname="on24" full_domain = 'https://www.on24.com' site_name="ON24"
Studying within the knowledge, we’re utilizing an export from GetSTAT which has a helpful report that means that you can examine SERPs on your key phrases earlier than and after.
This SERPs report is accessible from different rank monitoring suppliers like website positioning Monitor and Superior Internet Rating – no preferences or endorsements on my aspect!
getstat_ba_urls = pd.read_csv('knowledge/webinars_top_20.csv', encoding = 'UTF-16', sep = 't')
getstat_raw.head()
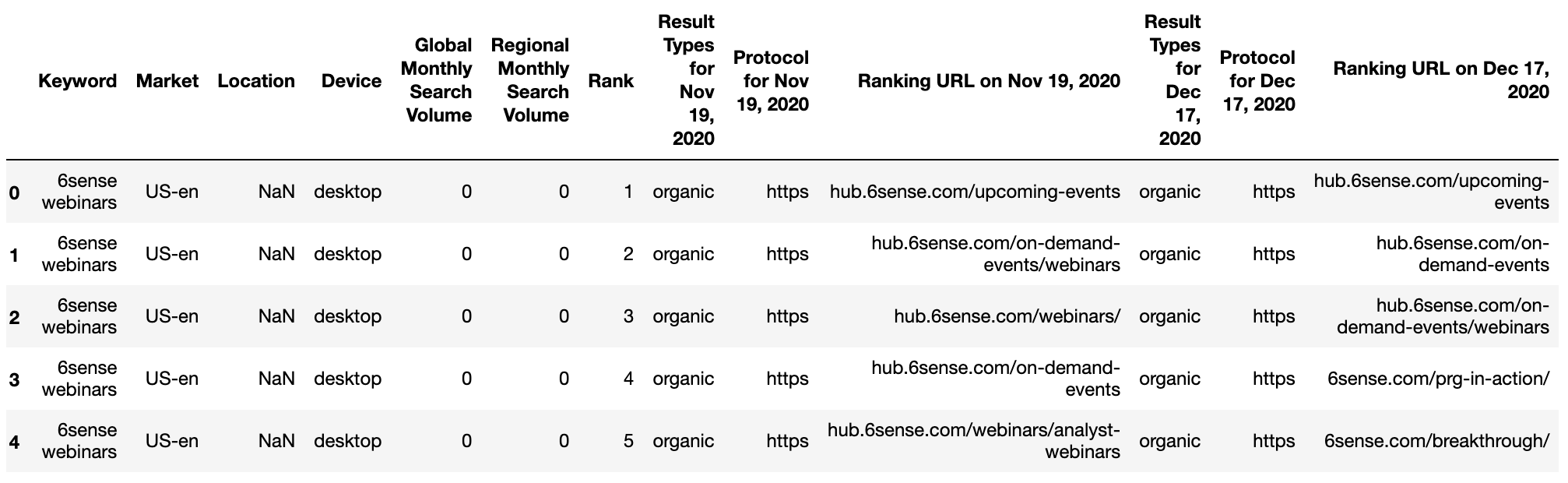 Screenshot by writer, January 2022
Screenshot by writer, January 2022getstat_ba_urls = getstat_raw
Assemble the URLs by becoming a member of the protocol and URL string to get the total rating URL for each earlier than the replace and after.
getstat_ba_urls['before_url'] = getstat_ba_urls['Protocol for Nov 19, 2020'] + '://' + getstat_ba_urls['Ranking URL on Nov 19, 2020'] getstat_ba_urls['after_url'] = getstat_ba_urls['Protocol for Dec 17, 2020'] + '://' + getstat_ba_urls['Ranking URL on Dec 17, 2020'] getstat_ba_urls['before_url'] = np.the place(getstat_ba_urls['before_url'].isnull(), '', getstat_ba_urls['before_url']) getstat_ba_urls['after_url'] = np.the place(getstat_ba_urls['after_url'].isnull(), '', getstat_ba_urls['after_url'])
To get the domains of the rating URLs, we create a replica of the URL in a brand new column, take away the subdomains utilizing an if assertion embedded in a listing comprehension:
getstat_ba_urls['before_site'] = [uritools.urisplit(x).authority if uritools.isuri(x) else x for x in getstat_ba_urls['before_url']]
stop_sites = ['hub.', 'blog.', 'www.', 'impact.', 'harvard.', 'its.', 'is.', 'support.']
getstat_ba_urls['before_site'] = getstat_ba_urls['before_site'].str.exchange('|'.be part of(stop_sites), '')
The listing comprehension is repeated to extract the domains submit replace.
getstat_ba_urls['after_site'] = [uritools.urisplit(x).authority if uritools.isuri(x) else x for x in getstat_ba_urls['after_url']]
getstat_ba_urls['after_site'] = getstat_ba_urls['after_site'].str.exchange('|'.be part of(stop_sites), '')
getstat_ba_urls.columns = [x.lower() for x in getstat_ba_urls.columns]
getstat_ba_urls = getstat_ba_urls.rename(columns = {'world month-to-month search quantity': 'search_volume'
})
getstat_ba_urls
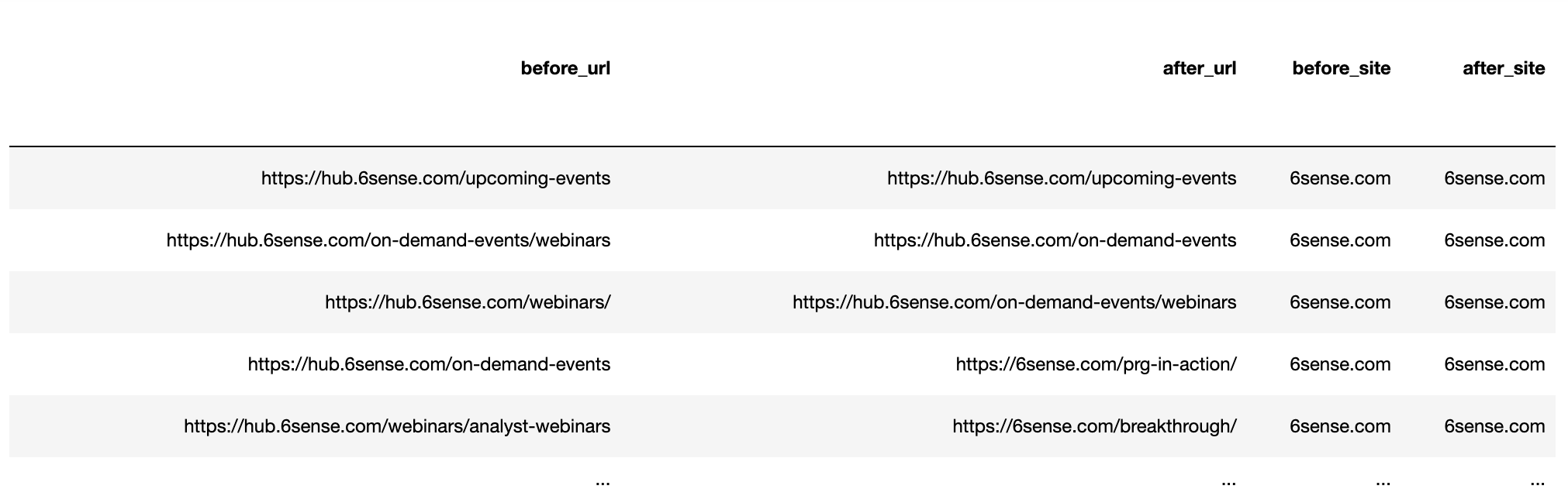 Screenshot by writer, January 2022
Screenshot by writer, January 2022Dedupe A number of Rating URLs
The subsequent step is to take away the a number of rating URLs by the identical area per key phrase SERP. We’ll cut up the info into two units, earlier than and after.
Then we’ll group by key phrase and carry out the deduplication:
getstat_bef_unique = getstat_ba_urls[['keyword', 'market', 'location', 'device', 'search_volume', 'rank',
'result types for nov 19, 2020', 'protocol for nov 19, 2020',
'ranking url on nov 19, 2020', 'before_url', 'before_site']]
getstat_bef_unique = getstat_bef_unique.sort_values('rank').groupby(['before_site', 'device', 'keyword']).first()
getstat_bef_unique = getstat_bef_unique.reset_index()
getstat_bef_unique = getstat_bef_unique[getstat_bef_unique['before_site'] != '']
getstat_bef_unique = getstat_bef_unique.sort_values(['keyword', 'device', 'rank'])
getstat_bef_unique = getstat_bef_unique.rename(columns = {'rank': 'before_rank',
'consequence varieties for nov 19, 2020': 'before_snippets'})
getstat_bef_unique = getstat_bef_unique[['keyword', 'market', 'device', 'before_snippets', 'search_volume',
'before_url', 'before_site', 'before_rank'
]]
getstat_bef_unique
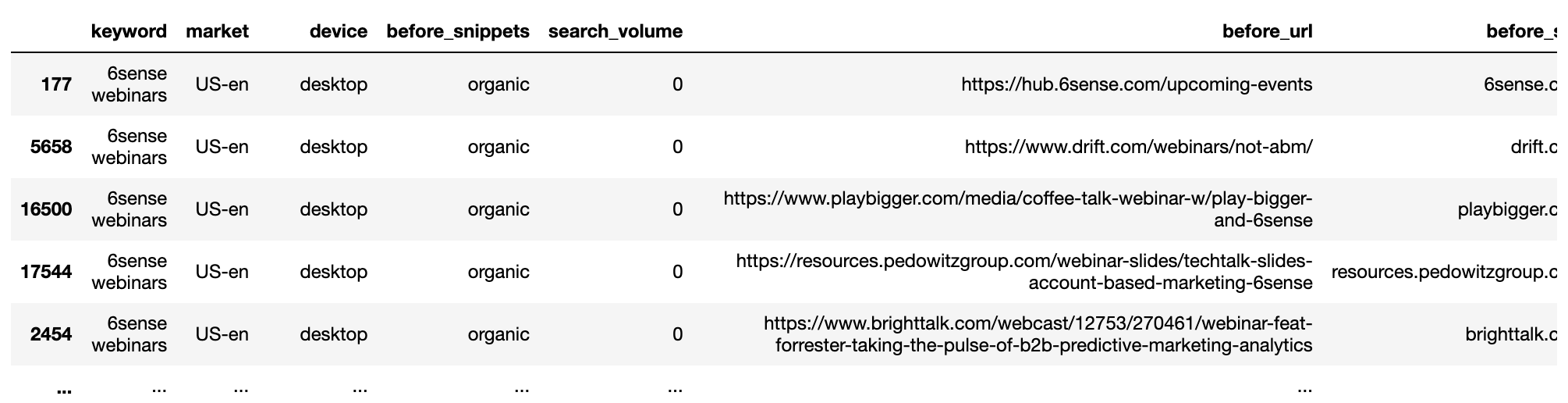 Screenshot by writer, January 2022
Screenshot by writer, January 2022The process is repeated for the after knowledge set.
getstat_aft_unique = getstat_ba_urls[['keyword', 'market', 'location', 'device', 'search_volume', 'rank',
'result types for dec 17, 2020', 'protocol for dec 17, 2020',
'ranking url on dec 17, 2020', 'after_url', 'after_site']]
getstat_aft_unique = getstat_aft_unique.sort_values('rank').groupby(['after_site', 'device', 'keyword']).first()
getstat_aft_unique = getstat_aft_unique.reset_index()
getstat_aft_unique = getstat_aft_unique[getstat_aft_unique['after_site'] != '']
getstat_aft_unique = getstat_aft_unique.sort_values(['keyword', 'device', 'rank'])
getstat_aft_unique = getstat_aft_unique.rename(columns = {'rank': 'after_rank',
'consequence varieties for dec 17, 2020': 'after_snippets'})
getstat_aft_unique = getstat_aft_unique[['keyword', 'market', 'device', 'after_snippets', 'search_volume',
'after_url', 'after_site', 'after_rank'
]]
Phase The SERP Websites
In terms of core updates, many of the solutions are usually within the SERPs. That is the place we will see what websites are being rewarded and others that lose out.
With the datasets deduped and separated, we’ll work out the widespread rivals so we will begin segmenting them manually which can assist us visualize the influence of the replace.
serps_before = getstat_bef_unique serps_after = getstat_aft_unique serps_before_after = serps_before_after.merge(serps_after, left_on = ['keyword', 'before_site', 'device', 'market', 'search_volume'], right_on = ['keyword', 'after_site', 'device', 'market', 'search_volume'], how = 'left')
Cleansing the rank columns of null (NAN Not a Quantity) values utilizing the np.the place() perform which is the Panda’s equal of Excel’s if system.
serps_before_after['before_rank'] = np.the place(serps_before_after['before_rank'].isnull(), 100, serps_before_after['before_rank']) serps_before_after['after_rank'] = np.the place(serps_before_after['after_rank'].isnull(), 100, serps_before_after['after_rank'])
Some calculated metrics to indicate the rank distinction earlier than vs after, and whether or not the URL modified.
serps_before_after['rank_diff'] = serps_before_after['before_rank'] - serps_before_after['after_rank'] serps_before_after['url_change'] = np.the place(serps_before_after['before_url'] == serps_before_after['after_url'], 0, 1) serps_before_after['project'] = site_name serps_before_after['reach'] = 1 serps_before_after
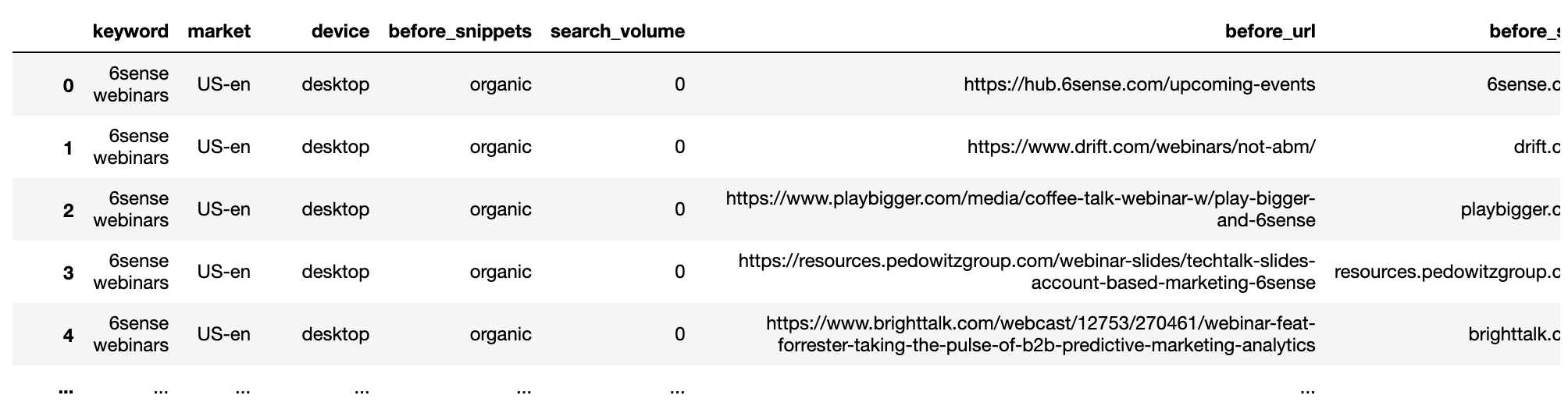 Screenshot by writer, January 2022
Screenshot by writer, January 2022Combination The Profitable Websites
With the info cleaned, we will now mixture to see which internet sites are probably the most dominant.
To do that, we outline the perform which calculates weighted common rank by search quantity.
Not all key phrases are as vital which helps make the evaluation extra significant in the event you care concerning the key phrases that get probably the most searches.
def wavg_rank(x):
names = {'wavg_rank': (x['before_rank'] * (x['search_volume'] + 0.1)).sum()/(x['search_volume'] + 0.1).sum()}
return pd.Collection(names, index=['wavg_rank']).spherical(1)
rank_df = serps_before_after.groupby('before_site').apply(wavg_rank).reset_index()
reach_df = serps_before_after.groupby('before_site').agg({'attain': 'sum'}).sort_values('attain', ascending = False).reset_index()
commonstats_full_df = rank_df.merge(reach_df, on = 'before_site', how = 'left').sort_values('attain', ascending = False)
commonstats_df = commonstats_full_df.sort_values('attain', ascending = False).reset_index()
commonstats_df.head()
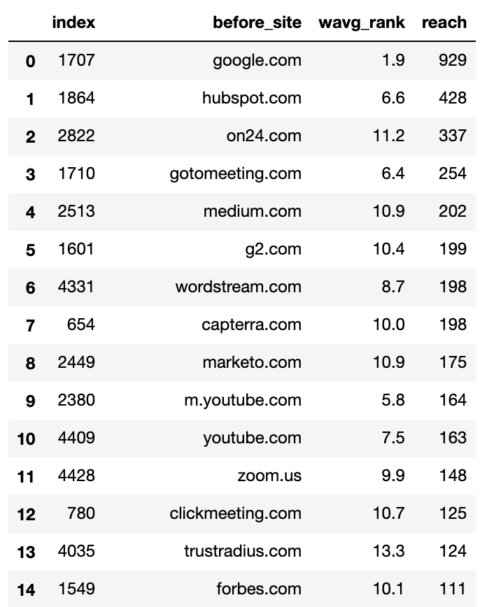 Screenshot by writer, January 2022
Screenshot by writer, January 2022Whereas the weighted common rank is vital, so is the attain as that tells us the breadth of the location’s presence in Google i.e. the variety of key phrases.
The attain additionally helps us prioritize the websites we wish to embrace in our segmentation.
The segmentation works by utilizing the np.choose perform which is sort of a mega nested Excel if system.
First, we create a listing of our situations.
domain_conds = [ commonstats_df['before_site'].isin(['google.com', 'medium.com', 'forbes.com', 'en.m.wikipedia.org', 'hbr.org', 'en.wikipedia.org', 'smartinsights.com', 'mckinsey.com', 'techradar.com','searchenginejournal.com', 'cmswire.com']), commonstats_df['before_site'].isin(['on24.com', 'gotomeeting.com', 'marketo.com', 'zoom.us', 'livestorm.co', 'hubspot.com', 'drift.com', 'salesforce.com', 'clickmeeting.com', 'qualtrics.com', 'workcast.com', 'livewebinar.com', 'getresponse.com', 'superoffice.com', 'myownconference.com', 'info.workcast.com']), commonstats_df['before_site'].isin([ 'neilpatel.com', 'ventureharbour.com', 'wordstream.com', 'business.tutsplus.com', 'convinceandconvert.com']), commonstats_df['before_site'].isin(['trustradius.com', 'g2.com', 'capterra.com', 'softwareadvice.com', 'learn.g2.com']), commonstats_df['before_site'].isin(['youtube.com', 'm.youtube.com', 'facebook.com', 'linkedin.com', 'business.linkedin.com', ]) ]
Then we create a listing of the values we wish to assign for every situation.
segment_values = ['publisher', 'martech', 'consulting', 'reviews', 'social_media']
Then create a brand new column and use np.choose to assign values to it utilizing our lists as arguments.
commonstats_df['segment'] = np.choose(domain_conds, segment_values, default="different") commonstats_df = commonstats_df[['before_site', 'segment', 'reach', 'wavg_rank']] commonstats_df
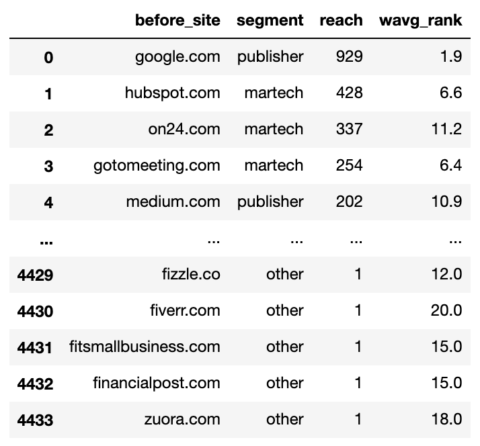 Screenshot by writer, January 2022
Screenshot by writer, January 2022The domains at the moment are segmented which suggests we will begin the enjoyable of aggregating to see which web site varieties benefitted and deteriorated from the replace.
# SERPs Earlier than and After Rank serps_stats = commonstats_df[['before_site', 'segment']] serps_segments = commonstats_df.phase.to_list()
We’re becoming a member of the distinctive earlier than SERPs knowledge with the SERP segments desk created instantly above to phase the rating URLs utilizing the merge perform.
The merge perform that makes use of the ‘eft’ parameter is equal to the Excel vlookup or index match perform.
serps_before_segmented = getstat_bef_unique.merge(serps_stats, on = 'before_site', how = 'left') serps_before_segmented = serps_before_segmented[~serps_before_segmented.segment.isnull()] serps_before_segmented = serps_before_segmented[['keyword', 'segment', 'device', 'search_volume', 'before_snippets', 'before_rank', 'before_url', 'before_site']] serps_before_segmented['count'] = 1 serps_queries = serps_before_segmented['keyword'].to_list() serps_queries = listing(set(serps_queries)) serps_before_segmented
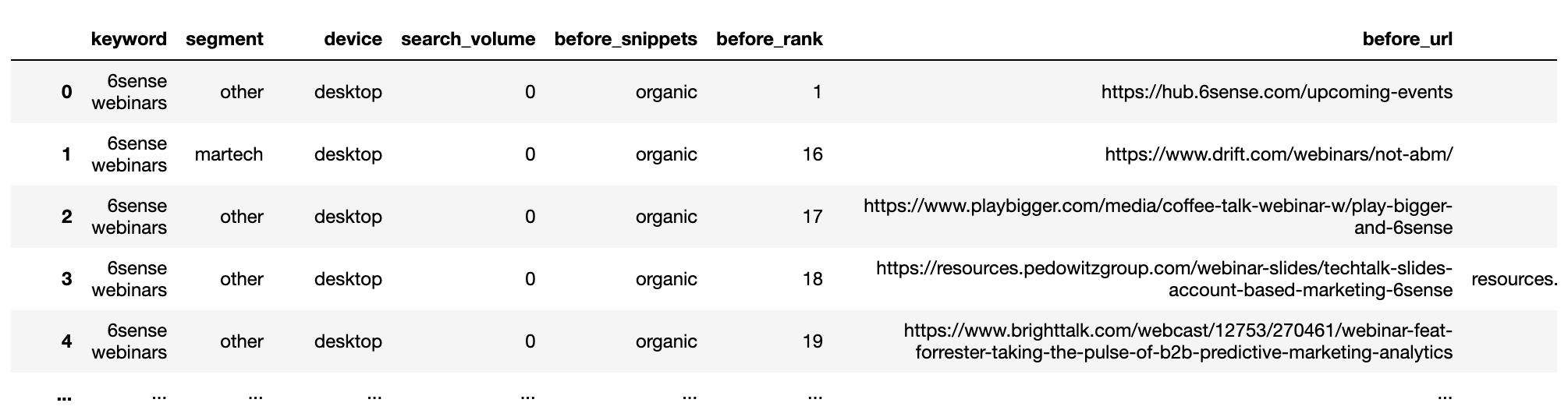 Screenshot by writer, January 2022
Screenshot by writer, January 2022Aggregating the earlier than SERPs:
def wavg_rank_before(x):
names = {'wavg_rank_before': (x['before_rank'] * x['search_volume']).sum()/(x['search_volume']).sum()}
return pd.Collection(names, index=['wavg_rank_before']).spherical(1)
serps_before_agg = serps_before_segmented
serps_before_wavg = serps_before_agg.groupby(['segment', 'device']).apply(wavg_rank_before).reset_index()
serps_before_sum = serps_before_agg.groupby(['segment', 'device']).agg({'depend': 'sum'}).reset_index()
serps_before_stats = serps_before_wavg.merge(serps_before_sum, on = ['segment', 'device'], how = 'left')
serps_before_stats = serps_before_stats.rename(columns = {'depend': 'before_n'})
serps_before_stats
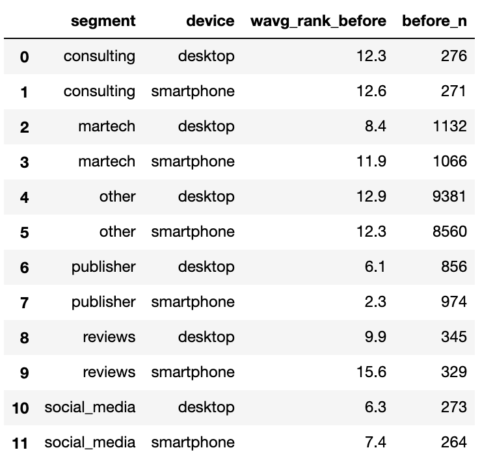 Screenshot by writer, January 2022
Screenshot by writer, January 2022Repeat process for the after SERPs.
# SERPs After Rank
aft_serps_segments = commonstats_df[['before_site', 'segment']]
aft_serps_segments = aft_serps_segments.rename(columns = {'before_site': 'after_site'})
serps_after_segmented = getstat_aft_unique.merge(aft_serps_segments, on = 'after_site', how = 'left')
serps_after_segmented = serps_after_segmented[~serps_after_segmented.segment.isnull()]
serps_after_segmented = serps_after_segmented[['keyword', 'segment', 'device', 'search_volume', 'after_snippets',
'after_rank', 'after_url', 'after_site']]
serps_after_segmented['count'] = 1
serps_queries = serps_after_segmented['keyword'].to_list()
serps_queries = listing(set(serps_queries))
def wavg_rank_after(x):
names = {'wavg_rank_after': (x['after_rank'] * x['search_volume']).sum()/(x['search_volume']).sum()}
return pd.Collection(names, index=['wavg_rank_after']).spherical(1)
serps_after_agg = serps_after_segmented
serps_after_wavg = serps_after_agg.groupby(['segment', 'device']).apply(wavg_rank_after).reset_index()
serps_after_sum = serps_after_agg.groupby(['segment', 'device']).agg({'depend': 'sum'}).reset_index()
serps_after_stats = serps_after_wavg.merge(serps_after_sum, on = ['segment', 'device'], how = 'left')
serps_after_stats = serps_after_stats.rename(columns = {'depend': 'after_n'})
serps_after_stats
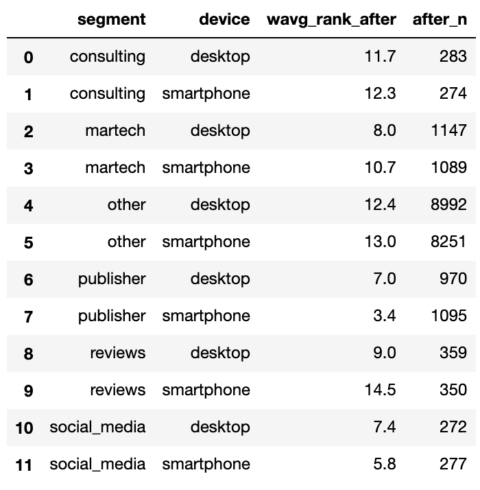 Screenshot by writer, January 2022
Screenshot by writer, January 2022With each SERPs summarised, we will be part of them and begin making comparisons.
serps_compare_stats = serps_before_stats.merge(serps_after_stats, on = ['device', 'segment'], how = 'left') serps_compare_stats['wavg_rank_delta'] = serps_compare_stats['wavg_rank_after'] - serps_compare_stats['wavg_rank_before'] serps_compare_stats['sites_delta'] = serps_compare_stats['after_n'] - serps_compare_stats['before_n'] serps_compare_stats
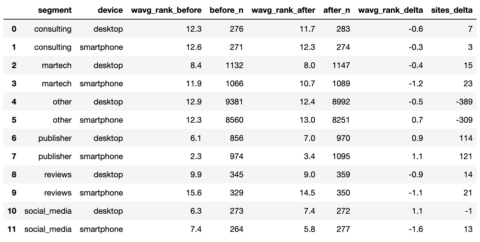 Screenshot by writer, January 2022
Screenshot by writer, January 2022Though we will see that writer websites appeared to realize probably the most by advantage of extra key phrases ranked for, an image would most actually inform a 1000 extra phrases in a PowerPoint deck.
We’ll endeavor to do that by reshaping the info into an extended format that the Python graphics bundle ‘plotnine’ favors.
serps_compare_viz = serps_compare_stats
serps_rank_viz = serps_compare_viz[['device', 'segment', 'wavg_rank_before', 'wavg_rank_after']].reset_index()
serps_rank_viz = serps_rank_viz.rename(columns = {'wavg_rank_before': 'earlier than', 'wavg_rank_after': 'after', })
serps_rank_viz = pd.soften(serps_rank_viz, id_vars=['device', 'segment'], value_vars=['before', 'after'],
var_name="section", value_name="rank")
serps_rank_viz
serps_ba_plt = (
ggplot(serps_rank_viz, aes(x = 'phase', y = 'rank', color="section",
fill="section")) +
geom_bar(stat="identification", alpha = 0.8, place = 'dodge') +
labs(y = 'Google Rank', x = 'section') +
scale_y_reverse() +
theme(legend_position = 'proper', axis_text_x=element_text(rotation=90, hjust=1)) +
facet_wrap('gadget')
)
serps_ba_plt
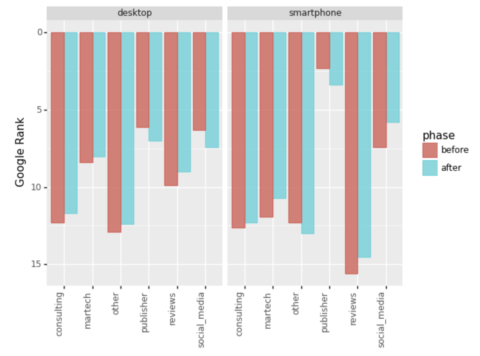 Screenshot by writer, January 2022
Screenshot by writer, January 2022And we’ve got our first visualization, which exhibits us how most web site varieties gained in rating which is just half of the story.
Let’s additionally take a look at the variety of entries into the highest 20.
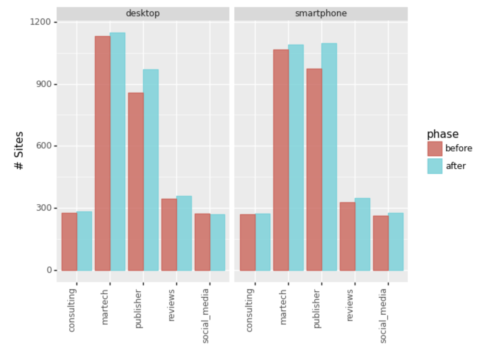 Screenshot by writer, January 2022
Screenshot by writer, January 2022Ignoring the ‘Different’ phase, we will see Martech and Publishers have been the principle winners increasing their key phrase attain.
Abstract
It took a little bit of code simply to create a single chart with all of the cleansing and aggregating.
Nevertheless, the ideas may be utilized to attain prolonged winner-loser views corresponding to:
- Area degree.
- Inner web site content material.
- End result Sorts.
- Cannibalised outcomes.
- Rating URL Content material varieties (blogs, supply pages and so on).
Most SERP reviews can have the info to carry out the above prolonged views.
Whereas it won’t explicitly reveal the important thing rating issue, the views can inform you a large number about what’s going on, aid you clarify the core replace to your colleagues, and generate hypotheses to check in the event you’re one of many much less fortunate ones trying to get better.
Extra assets:
Featured Picture: Pixels Hunter/Shutterstock
[ad_2]