| Dec 28, 2021 |
|
(Nanowerk Information) The analysis neutron supply Hein Maier-Leibnitz (FRM II) on the Technical College of Munich (TUM) is enjoying an vital function within the investigation of mRNA nanoparticles much like those used within the Covid-19 vaccines from distributors BioNTech and Moderna. Researchers on the Heinz Maier-Leibnitz Zentrum (MLZ) used the excessive neutron flux obtainable in Garching to characterize numerous formulations for the mRNA vaccine and thus to put the groundwork for bettering the vaccine’s efficacy.
|
|
The concept of utilizing messenger RNA (mRNA) as an lively ingredient is an excellent one: The molecule incorporates the particular blueprint for proteins that are then be synthesized by the cell. This makes it usually attainable to supply a really large spectrum of various therapeutically efficient proteins.
|
|
Within the case of the Covid-19 vaccine, these are the proteins of the attribute spikes on the floor of the Corona virus that are used for vaccination. The proteins are introduced on the floor of immune cells; then the human immune system triggers defenses towards these overseas proteins and thus towards the Corona virus. The mRNA itself is totally damaged down after only some hours, a truth which is advantageous to the security of those vaccines.
|
The highway to the very best packaging
|
|
The mRNA must be packaged appropriately with a view to preserve it from being damaged down on the best way to the cell by the ever-present enzymes of the human physique. That is executed utilizing nanoparticles which might encompass a mix of lipids or polymers.
|
|
The lipids are fats molecules much like the molecules of the cell membrane and assist deposit the mRNA within the inside of the cell. Lipids and biopolymers are then damaged down or excreted by the physique.
|
|
To this ends, the BioNTech formulation workforce led by Dr. Heinrich Haas labored along with the group led by Prof. Peter Langguth of the Pharmaceutical Know-how division on the Johannes Gutenberg College Mainz’s Institute of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences. They developed a sequence of formulations during which the nanoparticles consisted of varied mixtures of lipids and biopolymers already proved in prescription drugs.
|
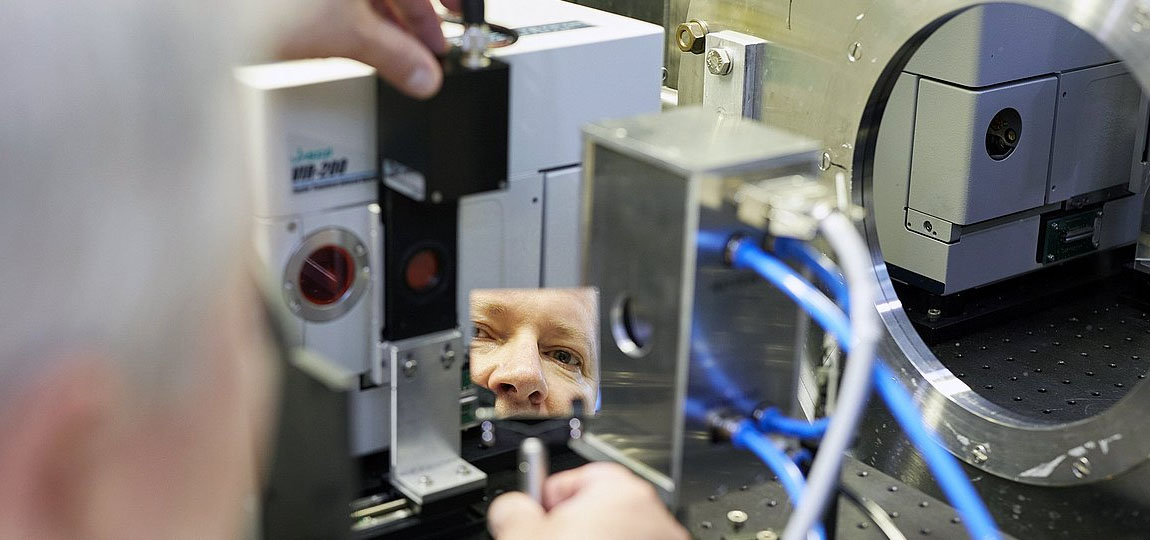 |
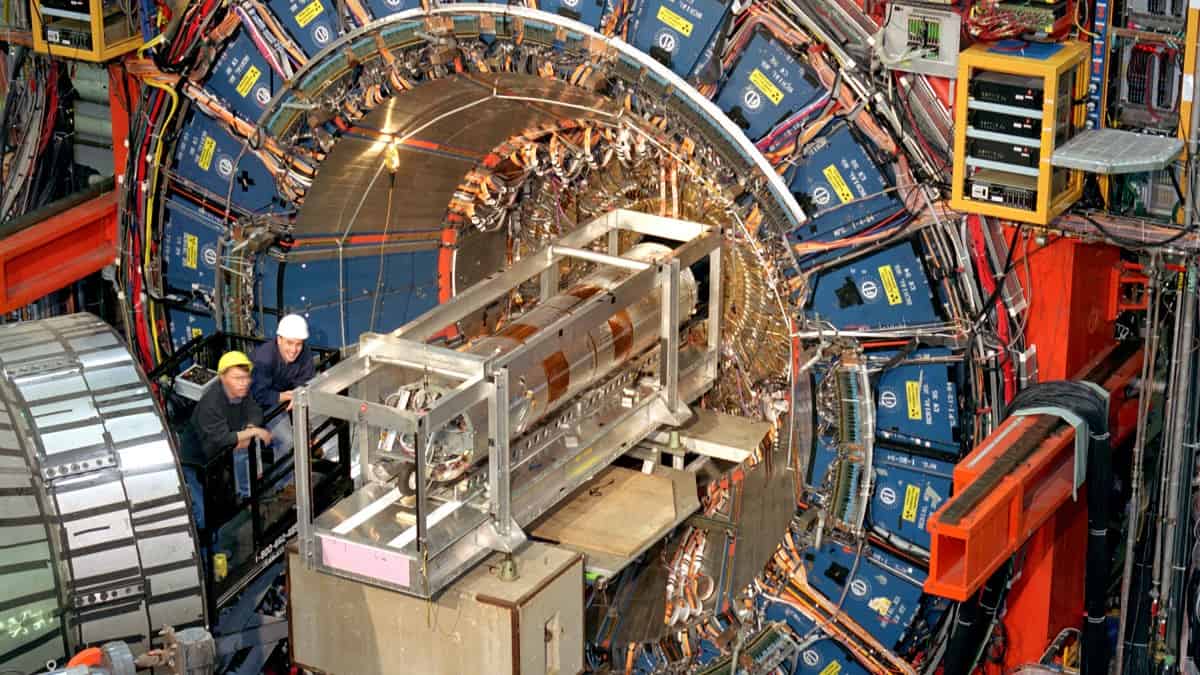
| Dr. Aurel Radulescu on the KWS-2 instrument of the Juelich Heart for Neutron Science (JCNS) within the analysis neutron supply Heinz Maier-Leibnitz (FRM II) of the Technical College of Munich. (Picture: Bernhard Ludewig / TUM / FRM II)
|
Within the mild of neutrons
|
|
With a view to examine the properties of variously composed nanoparticles with each other, the researchers subjected the nanoparticles to a variety of investigations. Along with x-ray and microscopic analyses, these investigations included radiation with neutrons utilizing the instrument KWS-2, operated by the Forschungszentrum Jülich on the FRM II of the Technical College of Munich in Garching.
|
|
The neutrons are scattered within the inside of the nanoparticles, inter alia, on the hydrogen nuclei and are deflected from their paths in a attribute method. That is the idea for conclusions about their distribution. If the hydrogen atoms of sure parts – for instance of the lipids solely – are exchanged with heavy hydrogen, the chemical properties and the pharmaceutical efficacy don’t change, however the scattering sample of the neutrons does.
|
|
“This methodology makes it attainable to selectively spotlight components of a fancy multi-component morphology with out altering the bodily chemistry of the pattern,” says Dr. Aurel Radulescu of the Jülich Centre for Neutron Science (JCNS), who’s chargeable for the instrument KWS-2 and who led the analysis of the measurement outcomes. “This makes it attainable to depict structural properties which different strategies can solely barely render seen, if in any respect.”
|
The precise diploma of order is the important thing
|
|
In these analyses the analysis groups had been serious about how effectively the assorted formulations had been capable of transmit the mRNA into the cell, known as transfection. The researchers thus came upon that the very best transfection charges had been achieved with nanoparticles which are characterised by a sure sort of inside association.
|
|
“Excessive ranges of organic exercise had been registered each time ordered and fewer ordered areas alternated within the inside of the nanoparticles in a attribute method. This may very well be a usually legitimate idea of structure-activity relationship which will be utilized independently of the methods investigated right here,” Dr. Heinrich Haas of BioNTech factors out. A equally low diploma of order had additionally been discovered beforehand by the analysis groups utilizing x-ray radiation in different lipid nanoparticles.
|
An improved process
|
|
With a view to obtain the specified structural properties lipids and biopolymers needed to be mixed with the mRNA utilizing precisely outlined procedures. Right here the analysis workforce was capable of present that the nanoparticles for packaging the mRNA may very well be produced in a single step, which implies a big simplification in comparison with the two-step process which was initially additionally investigated.
|
|
Thus a simplified methodology for the creation of mRNA nanoparticles with improved exercise was in the end discovered. “Such questions of sensible producibility characterize an vital prerequisite for the opportunity of creating pharmaceutical merchandise,” says Prof. Langguth. Sooner or later such ideas may very well be taken into consideration within the growth of recent mRNA-based therapeutic brokers.
|
Publications:
|
|
Hybrid Biopolymer and Lipid Nanoparticles with Improved Transfection Efficacy for mRNA. Christian D. Siewert, Heinrich Haas, Vera Cornet, Sara S. Nogueira, Thomas Nawroth, Lukas Uebbing, Antje Ziller, Jozef Al-Gousous, Aurel Radulescu, Martin A. Schroer, Clement E. Blanchet, Dmitri I. Svergun, Markus P. Radsak, Ugur Sahin and Peter Langguth. Cells 2020, 9(9), 2034 – DOI: 10.3390/cells9092034
|
|
Investigation of cost ratio variation in mRNA – DEAE-dextran polyplex supply methods. C. Siewert, H. Haas, T. Nawroth, A. Ziller, S. S. Nogueira, M. A. Schroer, C. E. Blanchet, D. I. Sverg, A. Radulescu, F. Bates, Y. Huesemann, M. P. Radsak, U. Sahin, P. Langguth. Biomaterials, 2019; DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.10.020
|
|
Polysarcosine-Functionalized Lipid Nanoparticles for Therapeutic mRNA Supply. S S. Nogueira, A. Schlegel, Ok. Maxeiner, B. Weber, M. Barz, M. A. Schroer, C. E. Blanchet, D. I. Svergun, S. Ramishetti, D. Peer, P. Langguth, U. Sahin, H. Haas. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 11, 10634–10645 – DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.0c01834
|