Searching for a hydrophilic nanoparticle resolution to antibiotic resistance
The Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention estimates that greater than 2.8 million People expertise antibiotic-resistant infections annually; greater than 35,000 die from these infections.
To handle this crucial and worldwide public well being challenge, a crew of researchers led by Hongjun (Henry) Liang, Ph.D., from the Texas Tech College Well being Sciences Middle (TTUHSC) Division of Cell Physiology and Molecular Biophysics, not too long ago investigated whether or not or not a collection of novel nanoparticles can kill among the pathogens that result in human an infection with out affecting wholesome cells.
The examine, “Hydrophilic Nanoparticles that Kill Micro organism whereas Sparing Mammalian Cells Reveal the Antibiotic Position of Nanostructures,” was revealed Jan. 11 by Nature Communications.
Previous analysis has proven that hydrophobicity (a molecule’s means to repel water) and hydrophilicity (a molecule’s means to draw and dissolve in water) impacts cells; the extra hydrophobic a substance is, the extra opposed the response it would trigger. Nevertheless, Liang mentioned, there isn’t a quantitative commonplace for the way a lot hydrophobicity is appropriate.
“Mainly, you may kill micro organism if you improve hydrophobicity,” Liang mentioned. “However it would additionally kill wholesome cells, and we do not need that.”
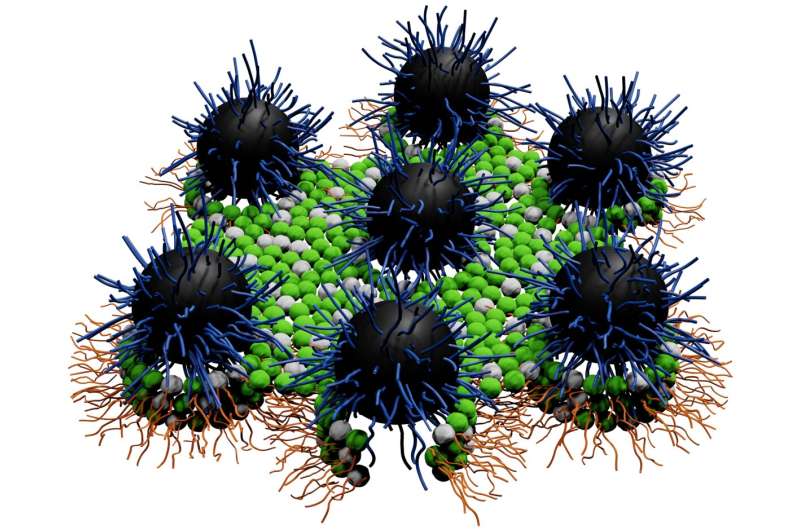
For his or her examine, the Liang crew used novel hydrophilic nanoparticles generally known as nanoantibiotics that have been developed by Liang’s laboratory. Structurally talking, these novel nanoantibiotics resemble tiny bushy spheres, every composed of many hydrophilic polymer brushes grafted onto silica nanoparticles of various sizes.
These artificial compounds, which Liang’s lab produces, are designed to kill micro organism by way of membrane disruptions like antimicrobial peptides do, however by way of a distinct mode of membrane transforming that damages bacterial membranes and never mammalian cells. Antimicrobial peptides are a various class of amphipathic molecules (partially hydrophilic-partially hydrophobic), which happen naturally and function the primary line of protection for all multicellular organisms. The direct use of antimicrobial peptides as antibiotics is restricted by their stability and toxicity.
There have been different research by which researchers grafted amphipathic molecules onto nanoparticles, and so they too kill micro organism. Nevertheless, Liang mentioned the first challenge in utilizing amphipathic molecules is that it turns into very tough to strike the fitting stability between their hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity in order that the toxicity of those molecules to our personal cells is considerably decreased.
“In our case, we take away that uncertainty from the equation as a result of we began with a hydrophilic polymer,” Liang identified. “The cytotoxicity of hydrophobic moieties just isn’t a priority anymore. These hydrophilic polymers by themselves, or the silica nanoparticles alone do not kill micro organism; they must be grafted onto the nanostructure to have the ability to kill micro organism. And so, that is the primary necessary discovery.”
The Liang crew additionally found that the diploma of antibiotic exercise is affected by the dimensions of the bushy spheres, which in line with Liang is the second necessary discovery of this analysis. These measuring 50 nanometers and beneath look like rather more energetic than these whose dimension exceeds 50 nanometers. Liang mentioned these measuring roughly 10 nanometers look like probably the most energetic. (Utilizing synchrotron small angle X-ray scattering and different strategies, the Liang crew is ready to interpret the molecular mechanism of the size-dependent antibiotic exercise.)
These discoveries are necessary as a result of utilizing nanoantibiotics to kill micro organism evades all identified mechanisms of bacterial resistance except micro organism utterly revamp their pathways for making cell membranes, which Liang mentioned is unlikely.
“Additionally it is almost unimaginable for micro organism to develop new resistance in opposition to the nanoantibiotics,” Liang emphasised. “Moreover, this discovery illuminates a blueprint to develop new antibiotics that may kill micro organism upon contact, however stay amiable to people as a result of they’re produced utilizing non-toxic and environmentally pleasant elements by way of nanoengineering.”
Yunjiang Jiang et al, Hydrophilic nanoparticles that kill micro organism whereas sparing mammalian cells reveal the antibiotic function of nanostructures, Nature Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-27193-9
Quotation:
Searching for a hydrophilic nanoparticle resolution to antibiotic resistance (2022, January 20)
retrieved 22 January 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-01-hydrophilic-nanoparticle-solution-antibiotic-resistance.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.